What is the WHO Surgical Safety Checklist?
The WHO Surgical Safety Checklist is a 19-item checklist used in operating rooms to reduce complications and patient deaths through improved communication and coordination among medical practitioners. Developed by the World Health Organization (WHO), it was published in 2008 after an extensive study that involved hospitals in 8 countries.
The WHO Surgical Safety Checklist was proven by multiple studies to help reduce post-operative death and morbidity and aid in promoting a culture of safety in surgical care. There are medical organizations that advocate its use and some even call for its mandatory enforcement after observing its impact on improving the safety of patients.
3 Main Sections of a Surgical Safety Checklist
Designed to be applicable worldwide, the surgical safety checklist developed by the WHO is divided into 3 sections designed to be conducted at 3 specific points during operation.
Briefing
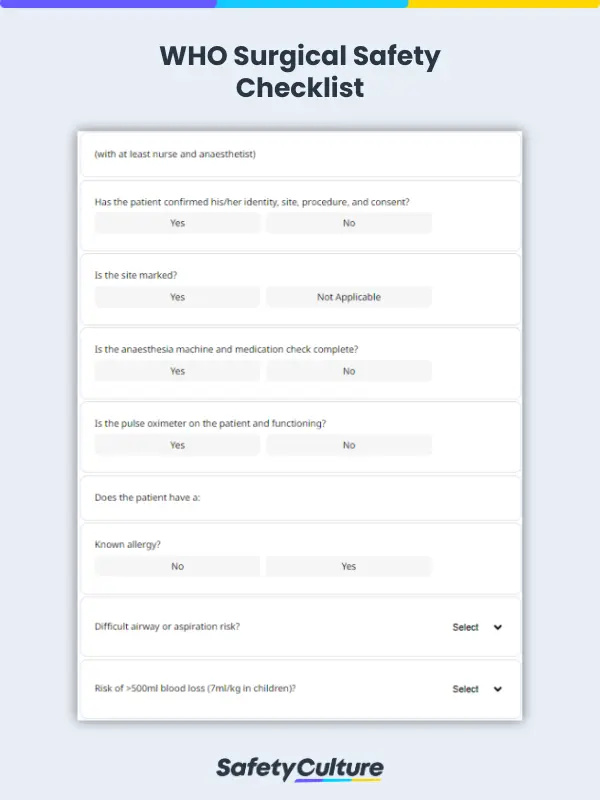
Done before the administration of anesthesia, this 7-item section of the surgical safety checklist is to be conducted in the presence of at least the nurse and anesthetist. The list of questions includes confirmation of known allergies, airway or aspiration risk, and blood loss.
Time-out
To be conducted before skin incision and in the presence of the nurse, anesthetist, and surgeon, this section specifies anticipated critical events and lists related questions to be answered by said medical professionals.
Debriefing
Done before the patient is allowed to leave the operating room, the nurse verbally confirms 4 items on the checklist. Finally, the surgeon, anesthetist, and nurse confirm any key concerns regarding the recovery and management of the patient.
5 Steps to Integrating the Use of a Surgical Safety Checklist
The importance of using a surgical safety checklist has already been established but there are still healthcare institutions that do not effectively implement its use in the operating room. Here are 5 steps to effectively integrate its use in your healthcare institution:
- Review the studies made on surgical safety checklists and understand the impact to patients.
- Get the buy-in of the medical professionals by presenting the studies and best practices in the medical field and mandate the use of surgical safety checklists in the healthcare institution.
- Perform internal audits to ensure that the surgical safety checklists are being used.
- Analyze the impact of the use/non-use of the surgical safety checklist in surgical care.
- Discuss the impact with the medical staff to reinforce the continued use of surgical safety checklists.