Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
4 min read
What is a Permit to Work System for Audit Checklist?
A Permit to Work System for internal audit checklist is a tool in ensuring that work activities are carried out safely and in accordance with established standards. This comprehensive checklist serves as a valuable tool for organizations looking to maintain a safe and compliant working environment.
Benefits of Using a Permit to Work System Audit Checklist
From enhanced safety measures to improved accountability and compliance with regulatory standards, this checklist can revolutionize your business operations :
Enhanced Safety Measures
By using the Permit to Work System Audit Checklist, you can ensure that every task is assessed for potential risks. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents and injuries, fostering a safer work environment for all employees.
Improved Accountability
Another key advantage of this checklist is that it assigns clear responsibilities to individuals involved in a particular task. This fosters a culture of accountability within your organization, ensuring that everyone understands their role in maintaining a safe and compliant workplace.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Adherence to safety standards is non-negotiable and at most, necessary. The Permit to Work System Audit Checklist is designed to align with industry-specific regulations such as OSHA, FDA, SEC, FTC, and so on. Ensuring that your organization remains compliant at all times can save you from potential fines and legal troubles.
Efficiency in Internal Auditing
Internal auditing is a critical process for evaluating the effectiveness of your safety protocols. With this checklist, you can streamline the auditing process. It provides a structured framework for assessing and improving your safety measures, making internal audits more efficient and effective.
Key Components of PTW System Audit Checklist
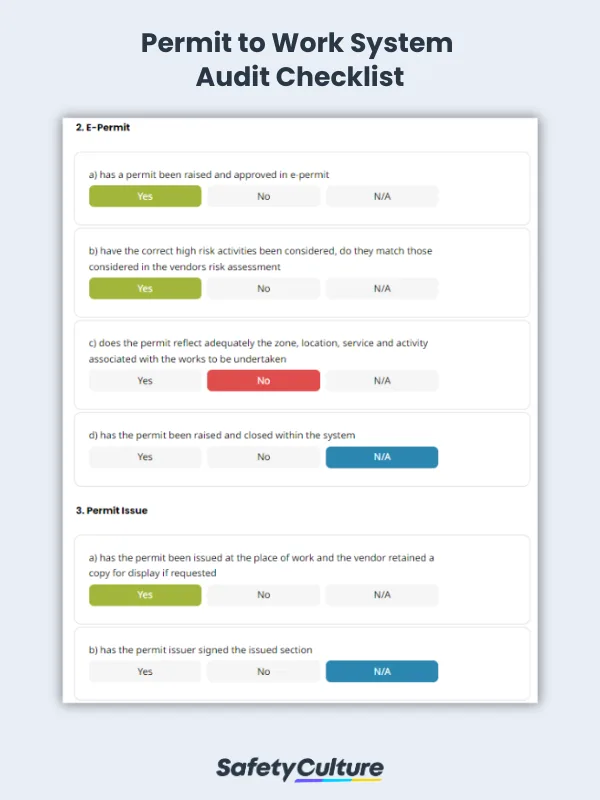
Defining the scope of the audit is crucial. It specifies which areas and processes related to the PTW system will be examined during the audit. A well-defined scope ensures that the audit is focused and comprehensive. Here are the key components of what a PTW system audit checklist would have :
Regulatory Compliance : The audit should evaluate whether the PTW system complies with relevant and applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
PTW Authorization Process : This component assesses the effectiveness of the PTW authorization process, including how permits are issued, reviewed, and approved. It ensures that only qualified personnel are allowed to perform hazardous tasks.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Identification : Auditors should examine how well the system identifies and assesses risks and hazards associated with the work to be performed. This is crucial for making informed decisions regarding safety measures.
Safety Measures and Precautions : The audit reviews the adequacy of safety measures and precautions outlined in the PTW. It ensures that the necessary controls are in place to mitigate identified risks.
Documentation and Recordkeeping : Maintaining comprehensive documentation and records of PTW activities is essential. Auditors verify whether records are properly maintained and easily accessible for review.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Use this Checklist
Before going into the checklist, gather all relevant documents, including work permits, safety procedures, and the PTW system itself. Ensure you have a clear understanding of the upcoming work and potential hazards.
Step 1: Start by reviewing the work request thoroughly. Ensure it is complete and contains all the necessary information. Verify if the work aligns with the organization’s safety policies and procedures.
Step 2: Identify potential hazards associated with the work. This step is crucial for risk assessment and control measures. Hazards can include electrical, chemical, or physical risks.:
Step 3: Assess the risks associated with each identified hazard. Use a risk assessment matrix to determine the level of risk. This step will help prioritize safety measures.
Step 4: Based on the risk assessment, define control measures to mitigate or eliminate hazards. These measures could include personal protective equipment (PPE), isolation procedures, or safety barriers.
Step 5: Once control measures are in place, issue the PTW. Ensure that all involved parties understand their responsibilities and the conditions of the permit.
Step 6: Renew the PTW if work continues beyond the initial permit period. Upon completion, close out the permit, documenting any incidents, near misses, or lessons learned.
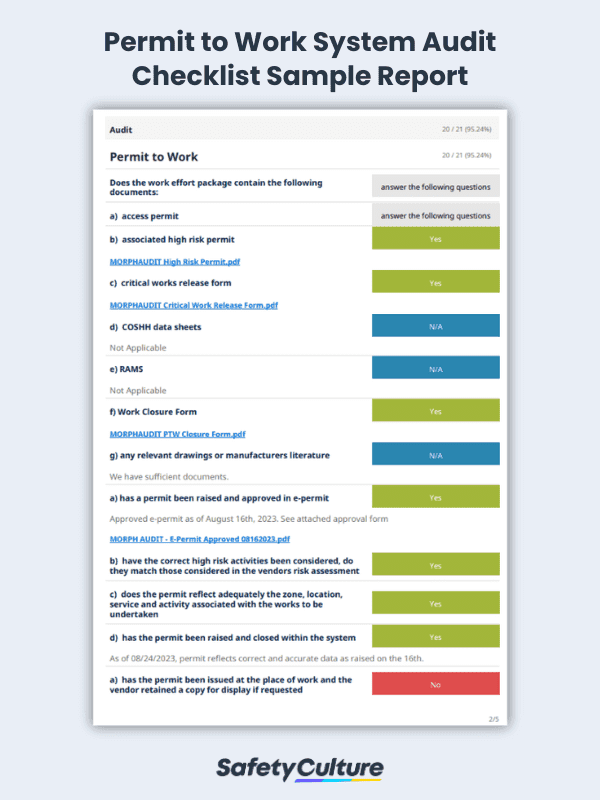
Permit To Work System Audit Checklist Sample Report | SafetyCulture
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.