How many great improvement ideas never leave your store floor?
Most managers see daily opportunities to improve. Find out why half of their ideas never take off.

Discover key grocery management strategies and best practices to optimize inventory, pricing, and customer experience.

Published 6 May 2025
Article by
6 min read
Grocery management is the comprehensive oversight of all facets within a grocery retail environment, including rigorous inventory management, strategic supplier supervision, and dynamic pricing optimization, to name a few. Aside from increasing revenues, cultivating a positive culture in this setting increases customer satisfaction, enhances employee loyalty, and guarantees regulatory compliance.
Grocery store operations have undergone significant transformations over the decades, from small, specialized shops to massive supermarkets with extensive options. This evolution reflects the shifts in consumer behavior, globalization of the supply chain, and technological advancements. Keeping up with these changes is vital to improve the business’s overall retail management system. Here’s why:
Boost cost-efficiency – Overstocking and stockouts , especially of perishable goods (e.g., food, medication), can be prevented through better demand forecasting and inventory optimization. Minimizing waste means lower overhead costs for the company.
Increase profitability – Thanks to actionable data, retailers can align stock levels with customer demand, supporting higher sell-through rates. Data-driven insights also facilitate other retail responsibilities and processes, like pricing, promotions, and product placement.
Improve operational flexibility – Adaptability is crucial in retail. Effective grocery management, encompassing employee scheduling and restocking, enables companies to become more agile in overcoming challenges.
Enforce regulations – With a comprehensive system, companies have the tools and processes necessary to meet regulatory requirements, from food and workplace safety to consumer data protection.
Enhance customer satisfaction – Ensuring product availability, preserving freshness, and improving services are guaranteed to maintain customer loyalty and attract potential clients. In fact, 84% of consumers are more likely to stick with a brand that offers a loyalty program, and 75% favor brands that understand them on a personal level.
Simplify store oversight, improve decision-making, and boost growth with an all-in-one platform for every aspect of your retail business.
Grocery store management is a multi-faceted process. It comprises different elements; each is necessary to uphold efficiency, meet customer expectations, and increase the profitability of their retail operations. These are five of the most crucial:
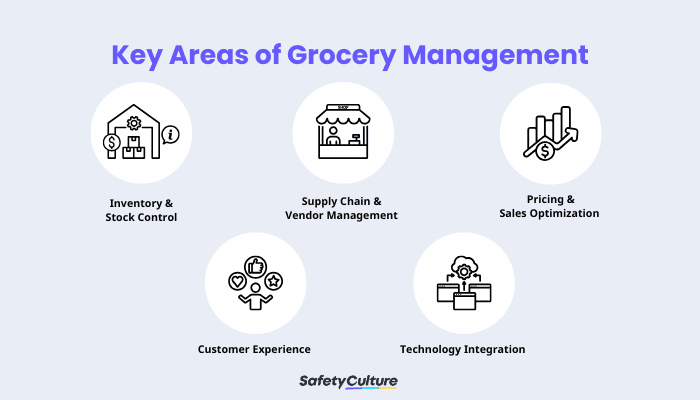
Grocery Management Framework
Ensuring optimal stock levels requires careful tracking, collaborative management, and prompt replenishment. This prevents two outcomes: wasteful, ergo expensive overstocking and frustrating-to-customers stockouts.
Supermarket chains have inventory management and tracking systems that detect low-stock items and trigger automatic replenishment. Keeping shelves stocked with high-demand products ensures customers get what they need.
Grocery products are often sourced from an array of suppliers. Coordinating deliveries, monitoring quality, and negotiating contracts maintains a reliable and cost-effective supply chain.
Top grocers uphold strict vendor management policies, ensuring all suppliers adhere to the company’s quality and sustainability standards. It also strengthens brand reputation and customer trust.
Setting competitive prices and adjusting them based on demand maximizes revenues while maintaining customer affordability. Demand forecasting improves stock control and helps balance discounts and promotions.
E-grocers and shops use dynamic pricing algorithms, based on factors such as competitor prices and customer demand. It’s also used by airlines, ticket sellers, and ride-sharing services.
Improving customer satisfaction means retention. Aside from training workers to provide better service, this element also involves optimizing the store layout to reduce checkout times, enhance convenience, and increase impulse buying tendencies.
Premium stores with sophisticated and international items have improved grocery operations by making their layouts more navigable. People flock to these shops because they track the customer journey carefully to improve their offerings.
Digital tools, such as Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven analytics, and self-serving kiosks, have greatly improved operations in this retail setting. Grocery management systems are must-haves in this day and age, streamlining numerous tasks from inventory tracking to automated checkouts.
Grocery stores should follow a structured approach to guarantee smooth operations, profitability, and customer satisfaction. Each step within the following guide is crucial for maintaining optimal stock, controlling costs, and improving the shopping experience:
Retail businesses should analyze sales trends, customer preferences, and seasonal variations to predict the quantity and type of products needed. Aside from ensuring that the right products are available at the right time through regular store audits, make sure that these are based on the grocery’s standards.
Vendors must be chosen based on reliability, pricing, and product quality. One of the most crucial aspects of handling vendor relationships and related tasks is order management. This ensures timely procurement and inventory replenishment.
Inventory tracking ensures that stock levels are monitored in real-time, while stock rotation minimizes product spoilage. One of the easiest and most popular strategies is FIFO (First In, First Out).
Maintaining an edge in the market requires setting competitive prices based on costs, demand, and competitor pricing. Managing profit margins ensures revenue goals are met while maintaining customer affordability.
Staff members should understand store processes, customer service expectations, and safety protocols. Aside from improving operational processes, providing training programs increases staff engagement and enhances productivity.
Designing a store layout that’s easy to navigate improves the customer’s overall shopping experience. It also allows staff members to provide better service, especially during checkout.
Retail businesses are subject to different regulations, including food safety, labor laws, and other industry standards. Proactive risk management identifies and addresses operational risks before they escalate.
Running a business in the retail sector is highly demanding due to the industry’s low margins and heavy competition. Despite following structured guidelines, some still face challenges that could threaten their future in the market. Get to know these potential threats and learn how to handle them:
Ineffective waste management – Since groceries handle perishable goods, overstocking leads to waste. Utilizing AI-driven analytics improves demand forecasting, even during seasonal demand fluctuations.
Supply chain disruptions – Any delay from suppliers will cause stock shortages. While diversification reduces reliance on a single vendor, building stronger relationships and negotiating long-term contracts are the most sound strategies.
Labor shortages – High employee turnover increases hiring and training costs. Offering competitive wages and incentives is one way to retain employees. Providing training gives workers a sense of ownership of the company, increasing their confidence and productivity.
Price sensitivity – Small retailers find it hard to compete with large enterprises. Focusing on a unique value proposition and implementing loyalty programs can help the business stay competitive.
Time-consuming admin work – Grocery managers spend hours each week fixing errors or chasing approvals. Streamlining routine tasks helps them focus on store performance, staff, and customer experience.
How many great improvement ideas never leave your store floor?
Most managers see daily opportunities to improve. Find out why half of their ideas never take off.

SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries, such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Leverage data analytics to forecast demand, plan strategies, build better relationships with suppliers, and make informed decisions regarding grocery operations. Reduce stockouts and minimize waste by streamlining inventory tracking, monitoring expiration dates, and automating replenishment. Improve operational efficiency, enhance productivity, and reduce costs through a unified platform.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Digital Tool
Operations

Learn about the types of forms your business can use to standardize processes, collect valuable and actionable data, and ensure compliance.
Logistics
Operations

Understand warehousing logistics and manage the storage, movement, and handling of inventory to effectively meet supply and demand.
Operations
Human Resources

Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.