Unlock hidden efficiency
Middle managers lose over 5 hours each week on low-value tasks—time that could be spent driving meaningful progress. Learn why they hold the key to operational success.

This guide will discuss: what process management is, why it’s important, and how teams can implement it in their operations.

Published 25 Nov 2025
Article by
7 min read
Process management is the practice of managing and optimizing the processes used to complete tasks and achieve goals. Also known as business process management (BPM), it involves understanding current systems and practices, identifying areas for improvement, and carrying out changes to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
With a better understanding of how your processes really work, you can spot what’s slowing teams down and fix it fast. Here’s how it helps:
Work faster - Streamlining processes reduces time and effort needed to complete tasks. This, in turn, leads to increased productivity and cost savings.
Stay adaptable - You can see where things get stuck and adjust plans to keep work accurate and efficient. This gives teams the tools to use their resources wisely.
Respond quicker to customers - Knowing the ins and outs of your systems and processes makes it easier to adjust your approach to changing demands and keep quality high.
Unlock hidden efficiency
Middle managers lose over 5 hours each week on low-value tasks—time that could be spent driving meaningful progress. Learn why they hold the key to operational success.

Before planning a BPM strategy, it’s important to understand its different types first. The approach will depend on the kind of process you need to deal with. Here are the three types of process management and examples that you might encounter:
System-centric – This type focuses on workflow orchestration at the core of business operations. The processes that fall under this category usually involve automation and technological tools—basically, those that function on their own without the help of humans. The ISO management system, for instance, falls under this category.
Human-centric – As opposed to the former type, this category of process management revolves around processes that require human expertise or interaction to implement. An example of this is a sorting operative for waste management.
Document-centric – The final type of process management is concerned with handling company records and documents. Processes that require administrative assistance usually belong in this category. One example of this is the procedure for preparing, keeping, and verifying contracts with suppliers.
Process management comes in a variety of approaches, each with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common BPM methods include:
Lean process management is a method that focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing efficiency. It revolves around the idea that any process can be improved by reducing the amount of time, effort, and resources required to complete it. This approach is often used in manufacturing and production settings.
Six Sigma helps teams cut down on errors and deliver higher quality work. By focusing on accuracy and consistency, you can improve processes and boost customer satisfaction. It’s especially useful for product development and customer service teams who want to get things right the first time.
Agile process management highlights flexibility and adaptability. It handles and improves processes by allowing for rapid changes and adjustments. For this reason, it works best in software development and IT environments.
Process management undergoes five key phases: assessment, design, implementation, monitoring, and optimization. This section outlines how each step works and how they fit in the process management framework.
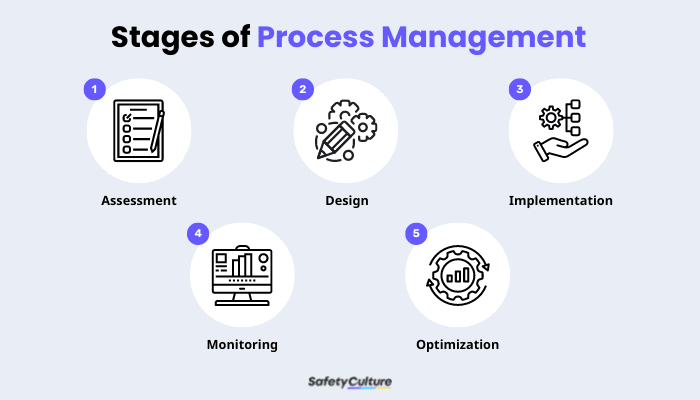
Start with an initial assessment of the organization’s current processes. Map out the details of existing procedures, identify the ones to be improved based on select performance metrics, and analyze which to prioritize among the least efficient options.
When sketching out current processes, consider the following questions:
How does the process work?
Who is in charge of this process?
How long does it take to complete this process?
How often is this process done?
After evaluating, develop a strategy to enhance a specific process. At this stage, teams will plan how the new process will ideally work from start to finish, along with additional information to supplement it. One good example is creating a flowchart to visualize things in a step-by-step fashion.
As an additional step, they can simulate how the new process will turn out in different scenarios before carrying it out in practice.
Once your process design’s complete, it’s time to put it into action. That could mean automating repetitive tasks or standardizing how work gets done. Some might need upgrades in technology, while others might call for changes in procedures, resource allocation, or training.
The process doesn’t end with implementing things on the ground. Since process management requires long-term commitment, consistent monitoring is vital to its success. Teams must track how their newly implemented process performs over a specific period. Gathering this information will help them determine which things work and which parts require change.
Continuous improvement is key for long-term process management strategies. Over a specific time frame, teams can further refine their newly established process using the data collected during the monitoring stage. This enables them to make informed decisions about changing certain parts of the process to improve its performance, keep up with the fast-paced changes in their industry, and satisfy customer needs.
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
Process management is by no means an easy task, and challenges can arise when attempting to implement it. Here are the most common areas where roadblocks can occur in managing business processes:
Getting stakeholders on board – Buy-in from stakeholders—from customers and suppliers to employees and management, among others—is a vital element in successful process management but can be difficult to achieve. After all, people may have varying opinions on how the process should be managed.
Setting unclear objectives and goals – These elements establish the purpose and direction in which things are headed. Thus, a process is bound to fail if the BPM strategy doesn’t clearly define the short- and long-term outcomes that it aims to achieve.
Communicating across teams – Successfully managing processes requires open communication among the members involved. Lacking this crucial factor can result in conflict and errors in carrying things out, which can cost the team productivity and efficiency.
Consistently following through processes – As the process evolves, it’s tough to keep everyone up to speed about the changes. Moreover, ensuring that the process is consistently followed and documenting changes can be tedious, especially in fast-paced environments.
Tracking performance metrics – Process management doesn’t stop once the process has been carried out; it must be monitored continuously to ensure its success. This task becomes daunting when there are multiple processes to check and no established benchmarks to measure success or failure.
Given the challenges mentioned above, how can leaders effectively manage their existing and prospective processes? Here are the best practices for effectively developing and managing business processes:
Involve key stakeholders in process management – Connecting with customers, suppliers, and partners in the process helps ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the process is being implemented correctly.
Anchor process goals on organizational operations – Establishing goals in this way allows teams to clearly define how the process aligns with the company’s business goals, which helps in setting their BPM strategy up on the right path.
Document all processes – Transparency is key to effective communication. For this reason, thoroughly documenting every step of the process , including all changes made, will help ensure that everyone in the organization is aware of the steps involved in each task and that they are being followed accurately.
Measure process performance – Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as completion time, cost, and customer satisfaction. Doing so helps pinpoint areas that require further work and ensure that things are running as efficiently as possible.
Regularly review and update processes – Holding periodic reviews of processes is key to ensuring that they are still relevant and effective for the current time and context.
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Operations
Business Processes

Learn how reliable process automation is key to safe, consistent operations and how it minimizes quality and compliance risks.
Logistics
Operations

Learn about the importance of transport and logistics within the supply chain and how it is used in business operations.
Logistics
Operations

Learn about transport network analysis and how network-level insight improves reliability and reduces operational risk.