Maintain Optimal Stock Levels with Inventory Replenishment
Master the inventory replenishment process to improve stock management, enhance supply chain efficiency, and maximize sales.

Published 17 Apr 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is Inventory Replenishment?
Inventory replenishment is the process of restocking products to maintain optimal inventory levels and meet customer demand. It involves monitoring stock levels, forecasting future sales, and coordinating with suppliers or distribution centers to ensure timely restocking. An effective inventory replenishment system is critical to retail businesses as it directly impacts sales and profitability.
A well-structured replenishment strategy ensures that high-demand products remain available while reducing the risk of overstocking slow-moving items. By optimizing inventory replenishment, retailers can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experience, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Purpose
In retail inventory management, strategic inventory forecasting and replenishment are crucial in maintaining the balance between overstocking and understocking. Here are the specific benefits of efficient inventory replenishment:
Prevents stockouts and lost sales – Inventory replenishment helps prevent stockouts , which occur when a product is unavailable, leading to lost sales and decreased customer satisfaction. By implementing effective inventory replenishment strategies, businesses can ensure that popular items are always in stock, meeting customer expectations.
Reduces excess inventory and storage costs – In 2022, the US retailers’ unsold stock grew by $78 billion , reaching approximately $740 billion. Implementing an efficient inventory replenishment strategy helps businesses avoid excess stock by aligning restocking with actual retail demand . This reduces warehouse expenses, minimizes waste , and improves cash flow for both retail and e-commerce operations.
Improves supply chain efficiency— A well-structured inventory replenishment process enhances coordination between suppliers , warehouses, and distribution centers. By leveraging automation and data analytics, businesses can streamline procurement and reduce lead times, resulting in a more agile and optimized supply chain .
Enhances customer satisfaction – Ensuring that popular products are always in stock leads to a better customer shopping experience , strengthening brand reputation and driving long-term customer retention. When customers can consistently find what they need, they’re more likely to return and recommend the business to others..
Supports business growth and profitability – Effective inventory replenishment allows businesses to scale operations efficiently by maintaining balanced stock levels. By maximizing operational efficiency and optimizing product availability, retailers can boost sales opportunities and sustain business growth.
Take Control of Your Inventory
Minimize stock discrepancies and streamline audits with real-time inventory tools. Stay ahead of demand with accurate tracking and forecasting.
Key Inventory Replenishment Strategies
Businesses can adopt various inventory replenishment strategies, but being on top of the important techniques for inventory replenishment helps build a more effective strategy. Retailers must choose the right one for each product category and follow its inventory replenishment best practices to maintain optimal inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Periodic Replenishment
This involves restocking inventory at fixed intervals, such as weekly or monthly, regardless of demand fluctuations. This replenishment strategy is ideal for products with predictable sales patterns and stable supply chains. While it simplifies inventory management, it requires accurate demand forecasting to avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Best Practices:
Use historical sales data and seasonal trends to determine the optimal replenishment frequency.
Conduct regular inventory audits to adjust order quantities and prevent excess stock buildup.
Continuous Replenishment
Also known as real-time replenishment, the continuous replenishment strategy involves restocking products as soon as inventory levels drop below a predefined threshold. It’s commonly used in grocery stores, e-commerce, and high-turnover retail environments. It ensures products remain available while minimizing excess inventory.
Best Practices:
Implement automated inventory tracking systems to monitor stock levels and trigger timely reorders.
Set accurate reorder points based on sales velocity and supplier lead times to prevent stockouts.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Replenishment
This strategy minimizes inventory holding costs by restocking items only when needed. This lean inventory approach reduces waste and optimizes cash flow but requires strong supplier relationships and precise demand forecasting. JIT is widely used in manufacturing, but retailers also use this replenishment approach.
Best Practices:
Strengthen collaboration with suppliers to ensure fast and reliable deliveries.
Utilize demand forecasting tools and real-time data analytics to align replenishment with actual sales trends.
Top-off Replenishment
Top-off replenishment involves restocking partially depleted inventory before it runs out, often during scheduled restocking windows. This method is common in warehouses, grocery stores, and retail chains to ensure shelves remain consistently stocked without causing disruptions.
Best Practices:
Plan replenishment during low-traffic hours to minimize operational disruptions and enhance efficiency.
Use sales and stock movement data to identify which products require frequent top-off replenishment.
The Inventory Replenishment Process
Implementing an efficient inventory replenishment policy ensures that businesses maintain optimal stock levels, prevent stockouts, and reduce excess inventory. Regardless of the chosen replenishment strategy, the following steps help streamline operations and enhance supply chain efficiency:
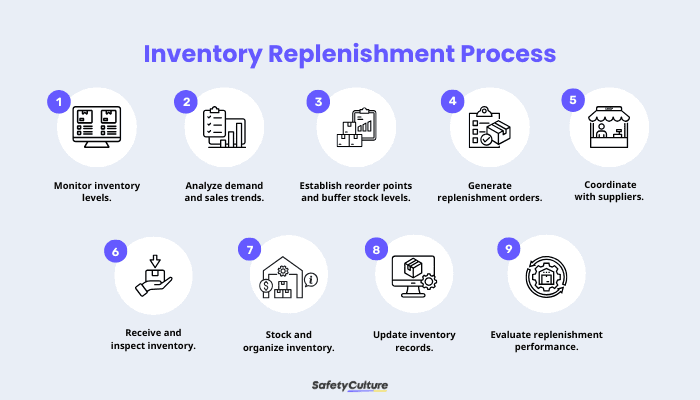
Inventory Replenishment Process
1. Monitor inventory levels.
Regularly track stock levels using inventory management software, Point-of-Sale (POS) systems, or manual audits. Accurate monitoring helps identify which products need replenishment and prevents shortages or overstocking. Implementing automated tracking systems reduces human error and provides real-time stock visibility, ensuring a more responsive inventory replenishment process.
2. Analyze demand and sales trends.
Review historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market demand to determine accurate replenishment quantities. Demand forecasting tools can help predict future sales and adjust stock levels accordingly. Factoring in external influences such as market trends, promotions, and competitor activity helps retailers make data-driven replenishment decisions.
3. Establish reorder points and buffer stock levels.
Set reorder points based on sales velocity and supplier lead times. Maintaining a safety stock buffer ensures that products remain available even during demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions. Regularly reassessing reorder thresholds helps businesses adapt to changing demand patterns and avoid stock imbalances.
4. Generate replenishment orders.
Once the stock reaches the reorder point, create the purchase orders or automated replenishment requests. Ensure that order quantities align with forecasted demand to optimize inventory turnover. Streamlining order processing with automated procurement tools reduces delays and improves order accuracy.
5. Coordinate with suppliers and distribution centers.
Work closely with suppliers, manufacturers, or distribution centers to confirm order details, delivery schedules, and lead times. Strong supplier relationships help ensure timely replenishment and minimize delays. Establishing alternative supplier options can mitigate risks caused by unexpected supply chain disruptions.
6. Receive and inspect inventory.
Upon delivery, verify the accuracy and quality of the received stock. Conduct thorough inspections to check for discrepancies, damages, or expired products before updating inventory records. Implementing barcode scanning or Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) technology ensures faster and more accurate inventory verification.
7. Stock and organize inventory.
Efficiently store replenished products in warehouses, stockrooms, or retail shelves based on demand frequency and accessibility. Implement proper inventory labeling and categorization to streamline order fulfillment. Using a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) system helps prevent product expiration and reduces waste, especially for perishable goods.
8. Update inventory records.
Immediately update inventory management systems to reflect new stock levels. Real-time inventory tracking helps maintain accuracy and prevents overordering or understocking. Regular system audits and integration with sales data ensure a seamless flow of inventory information across departments.
9. Evaluate inventory replenishment performance.
Regularly assess replenishment efficiency by analyzing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as stock turnover rate, order accuracy, and supplier reliability. Adjust strategies as needed to improve overall supply chain performance. Continuous process optimization, driven by data insights, helps businesses reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
Optimize Your Replenishment Process with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Promote a culture of accountability and transparency within your organization where every member takes ownership of their actions. Enhance ABC inventory classification accuracy, unify operational workflows, and maximize inventory efficiency using replenishment analytics through a unified platform.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Logistics
Operations

Warehousing Logistics (Storage Logistics)
Understand warehousing logistics and manage the storage, movement, and handling of inventory to effectively meet supply and demand.
Operations
Human Resources

The Role of HR in Workplace Health and Safety Management
Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.
Operations
Performance Evaluation

The RICE Framework: A Strategic Approach to Prioritization
Learn how the RICE framework and prioritization method helps put focus on high-ROI tasks to streamline workflows.