A Comprehensive Guide to Lockout Tagout (LOTO)
Learn more about the lockout tagout procedure: the meaning, devices used, steps to take, and core components to include for an effective LOTO program.

Published 26 Nov 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is Lockout Tagout?
Lockout tagout is a protection system against unintentional exposure to hazardous energy from equipment and machinery. A lockout device, such as a padlock, secures the energy isolating device while a tagout device (i.e. a tag) warns employees not to use the equipment.
Without proper LOTO procedures, workers risk severe injuries or even fatalities from unexpected machine startups or the sudden release of stored energy, turning routine maintenance into a deadly hazard.
Importance
One of the most common workplace hazards is the release of hazardous energy during maintenance or repair work on machinery or equipment. This can result in serious injuries or even fatalities if proper safety procedures are not followed. One important safety measure to prevent such accidents is the implementation of lockout tagout (LOTO) procedures. By locking and tagging the machinery or equipment and isolating it from energy sources, LOTO reduces the risks of accidents and injuries. It also reduces the need for costly repairs or replacements and extends the lifespan of equipment.
Establishing an efficient and safe LOTO program is crucial for organizations to protect their workforce and ensure compliance with occupational safety regulations. Without a well-defined LOTO procedure, employees may be unaware of the dangers posed by uncontrolled hazardous energy, increasing the likelihood of workplace incidents. A strong LOTO program not only enforces proper safety protocols but also fosters a culture of accountability and awareness.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
LOTO Standards
Lockout Tagout and Machine Guarding
Though the machine guarding standard covers exposure to hazardous energy during normal production operations, it is important to remember that the OSHA lockout tagout standard ( instead of the machine guarding standard ) will apply during normal production operations if:
the employee is required to bypass or remove machine guarding
the employee could be injured due to the sudden energization of equipment
OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard
The OSHA lockout tagout standard generally applies to any activity in which the sudden energization or startup of equipment and machinery could harm employees.
What are LOTO Devices?
Employers are required by the OSHA standard to provide lockout tagout devices that are durable, standardized, substantial, and identifiable. LOTO devices cannot be reused. The following information is primarily based on the OSHA lockout tagout standard:
What is an Energy Isolating Device?
These devices help ensure that energy isolation points are secure.

Energy Isolating Device
Energy isolating devices DO NOT INCLUDE push buttons, selector switches, and other control circuit type devices.
What is a Lockout Device?
A lockout device is a device that utilizes a positive means to hold an energy isolating device in a safe position and prevents the energization of equipment and machinery. Examples of lockout devices are padlocks, blank flanges, and bolted slip blinds.
Padlocks
In contrast to ordinary padlocks, these must be issued and standardized by the employer. They must only be used for lockout purposes and are distinguishable from all other types of padlocks in the workplace. Key-retaining padlocks are best for lockout purposes to ensure that the padlock is locked before the key can be removed.

Lockout Device
What is a Tagout Device?
A tagout device is a prominent warning device that can be securely fastened to an energy isolating device and indicates that both the equipment and the energy isolating device cannot be operated.
Tags
Tags are vital because they act as warnings against potential hazardous conditions when equipment or machines are energized. They provide vital information on the lockout condition of equipment in maintenance and can even contain a photo of the one responsible for specific equipment.

Tagout Device
What is a LOTO Box?
Also known as a lockbox or a group lockout box, a LOTO box is used when equipment has several isolation points that need to be secured (with their own energy isolating, lockout, and tagout devices) before it can be locked out. This is referred to as a group lockout or a group isolation.

LOTO Box
7 Steps of Lockout Tagout Procedure
A lock out tag out procedure is a list of steps taken in the workplace by different industries to help keep machines and equipment from unintentional energization while they are under maintenance or repair. Also known as LOTO steps, follow this comprehensive guide on how to properly shut down equipment:
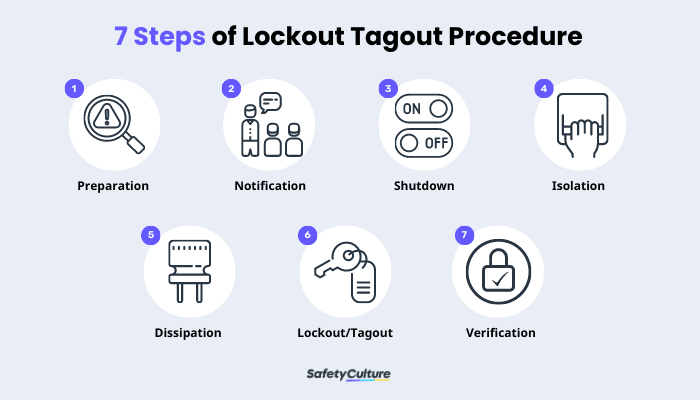
Step 1: Preparation – During this stage, the authorized employee should investigate to identify the equipment, machine, or process to be shut down. As a safety measure, this step should also recognize which energy resources must be controlled and highlight all the potential hazards that come with it.
Step 2: Notification – In the second stage, all affected personnel should be notified of the shutdown. Essential items to communicate can include information such as the equipment to be locked out, the reason behind it, the estimated time frame of the shutdown, the authorized personnel for the shutdown, as well as who to contact for clarifications and questions.
Step 3: Shutdown – After the planning stage, the actual equipment shutdown begins. For this process, follow the shutdown procedures established by the manufacturer or the workplace itself. Turn off the controls and make sure that all the running parts of the equipment come to a total stop.
Step 4: Isolation – This stage, also called de-energization—is the part where the authorized person will be needing to remove the equipment from any energy sources it is connected to. Some equipment may need to be shut down by turning off power from the breaker or by simply shutting a valve.
Step 5: Dissipation – In simpler terms, this is the process of removing possible residual energy still in the equipment. Depending on the type of equipment or power source, residual energy can either be disconnected, restrained, relieved, or made non-hazardous.
Step 6: Lockout/Tagout – During this actual lockout/tagout stage, the equipment is locked using energy-isolating devices. The tag to be attached, meanwhile, should contain the name of the person who performed the lockout and other additional information needed.
Step 7: Isolation verification – In this last stage, all the steps conducted have to be re-checked to ensure that everything is as it should be. Treat this as an opportunity to test the equipment by activating the process controls and observing the result. Non-activation of the equipment is a confirmation that energy isolation is completed.
Establishing a Safe Lockout Tagout Program
To be OSHA-compliant, a lockout tagout program must have 3 core components:
Lockout Tagout Inspections
The periodic inspection process involves meticulous assessment of equipment and machinery to ensure they are properly locked and tagged out before maintenance or servicing activities. LOTO inspections aim to prevent accidental energy releases, such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic, which could pose severe risks to the safety of workers.
Create your own LOTO Inspection checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Lock Out Tag Out Training
Since lockout tagouts have different levels of access, there are also different levels of training required for each type of access:
For authorized employees, training must include hazardous energy sources, the type and magnitude of hazardous energy, and methods for energy isolation and control.
For affected employees, training must include the purpose and use of LOTO procedures.
For other employees who are or could be in the area that LOTO procedures are being applied, training must include prohibition rules on restarting equipment that is locked out.
LOTO Safety
To go beyond compliance and truly build a robust lockout tagout program, safety supervisors must actively promote and sustain LOTO safety by doing the following:
Clearly define and communicate the lock out tag out policy.
Create a system for submitting and receiving LOTO reports.
Perform frequent LOTO audits.
Enforce lock out tag out documentation.
Perform Efficient LOTO with SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
Streamline safety procedures, improve compliance, and minimize risks associated with hazardous energy. With the SafetyCulture digital inspection platform, teams can create standardized LOTO checklists, conduct real-time audits, and ensure proper documentation of lockout procedures.
Optimize your organization’s operations and workflow with SafetyCulture. Our digital platform enables you to:
Simplify processes by automating manual and repetitive tasks
Maintain safety, quality, and compliance standards with digital checklists
Create powerful workflows by integrating your existing systems and software
Gain greater visibility and transparency with real-time reporting
Take advantage of our comprehensive features to transform your organization’s capabilities towards operations excellence.
FAQs About Lockout Tagout
Article by
SafetyCulture Content Team
SafetyCulture Content Contributor, SafetyCulture
View author profileRelated articles
Environmental Safety
Safety

Oil Drum Storage: Safety Guide and Best Practices
Learn the practices for safe oil drum storage, its importance, and the regulations for compliance.
Environmental Safety
Safety

Flood Risk Management
Read this guide to flood risk management, its importance, and the key components and strategies for this process.
Environmental Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Stormwater Pollution Prevention Best Management Practices (SWPPP BMP)
Learn about the types of best management practices for SWPP and the steps to effectively implement them in prevention plans.