Heijunka: Reduce Unevenness in the Production Process
Discover how Heijunka can help with production workflow. Take a look at ways of leveling production and an example of how to perform Heijunka

Published 9 Apr 2025
Article by
4 min read
What is Heijunka?
Heijunka is a lean manufacturing method that helps reduce overproduction by processing orders based on customer demand and avoiding bulk production in batches. It is a Japanese term for “leveling”, which allows organizations to optimize their inventory management system to meet customer needs and depend on customer buying rates. Heijunka is one of the thirteen pillars of the Toyota Production System and was established to save production costs and reduce unevenness in a production process.
What are the Advantages of Implementing Heijunka?
Heijunka in lean manufacturing aims to improve production workflow to better match the customer orders, reduce wastes, and minimize the chance of overburden. It helps the organization to achieve the following:
efficiently meet customer demands;
reduce inventory needs due to lesser batching process;
decrease capital costs;
increase profitability; and
minimize manpower issues.
Drive Excellence in Manufacturing Quality
Raise the bar for product quality and exceed customer expectations with standardized checks across all production sites.
Two Ways of Leveling Production
Proper implementation of Heijunka provides predictability, flexibility, and stability in the organization. It helps level the demand, decrease changeover time, and average the production volume and type in the long term. There are two ways of leveling production using the Heijunka concept, it can be implemented by volume or type.
Leveling by Volume – deals with the number of items per type of product produced in each batch. It helps to see what products should be prioritized according to customer demand.
Leveling by Type – adds different sequences of what product is being produced in every batch. It maintains the needed variety of products to be produced on a weekly or monthly basis.
Heijunka Example
Scenario: A garment manufacturing company is producing different types of women’s clothes that include blouses, dresses, and coats and there is a demand for 100 products in a month. The operation is Monday to Friday for 6 hours per day. Each product requires 1 hour to finish in production.

In normal manufacturing production, they intended to produce products in batches and prioritize the production of the product with the higher demand. What they will do is produce blouses until they meet the monthly demand, then proceed to the next item in the line. The production pipeline would look like this:

In this kind of production process, they saw an issue in terms of customer demand. What would they do if the customer ordered 1 blouse, 1 dress, and 1 coat?. In this type of production pipeline, the customer can get her order by day 15 as the production of the coat will start on day 15. Also, what if the demand for coats increases due to weather changes? By implementing the Heijunka concept which aims to level the production, instead of producing products by batches based on monthly demand, they divide it into weekly production and create a variety of products in a week to sustain the demand of the customers on a weekly basis.
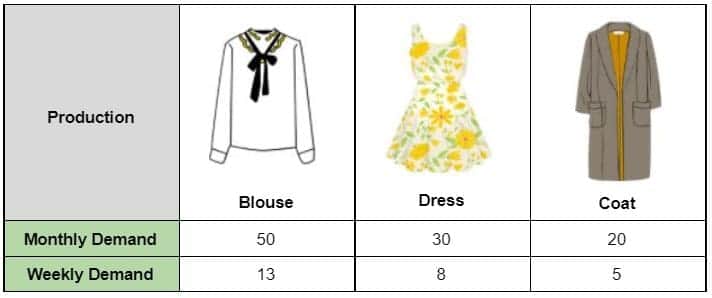
The production would look like this:

By doing this the team can produce the customer order of 1 blouse, 1 dress, and 1 coat on day 4, whereas in the previous case it can be delivered on day 15. On the other hand, if the demand changes in the next weeks, they can simply change the production pipeline and create a new set of lined up products to be produced based on trend and customer demand.
In implementing the Heijunka concept, the organization should also consider the factors that would affect the production timeline including the concept of Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED). It would help in analyzing the situation if it would be difficult or it would take more time for operators to switch on producing one product into another than the usual time it takes.
Apply the Heijunka Method using SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents✓ Boost productivity and efficiency✓ Enhance communication and collaboration✓ Discover improvement opportunities✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs about Heijunka
Related articles
Quality Management
Quality

Critical to Quality (CTQ): Guide to Customer-Driven Excellence
Learn the basics of Critical to Quality, its benefits, parameters, and specific applications in this comprehensive guide.
Quality
Quality Management

A Guide to Understanding Management Reviews
Learn about what a management review is, its importance, its key inputs and outputs, its process, and some FAQs.
Quality
Quality Management

5 Core Tools of Quality: The Ultimate Guide
Learn how the 5 core tools of quality work together to reduce risk, improve consistency, and drive continuous operational improvement.