Ensuring Worker Safety Through Construction Fall Protection
Discover the essential strategies and systems for construction fall protection to keep workers safe and comply with regulations.

Published 9 Aug 2024
Article by
6 min read
What is Construction Fall Protection?
Construction fall protection is a set of systems and practices used to prevent falls or mitigate injuries resulting from accidental falls, protecting workers in the construction industry or those involved in construction-related work. It includes measures such as installing guardrails and safety nets, using specialized personal protective equipment like fall arrest harnesses, and conducting extensive training to ensure safety while working at heights.
Why is Construction Fall Protection Important?
Slips, trips, and falls are the most common serious injuries in construction, resulting in long-term health issues and significant financial burdens.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), construction has the second most workplace deaths. In 2022, over 400 of 1,000 fatalities from this industry resulted from falls. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) also has sufficient statistics showing that construction is the most dangerous industry in the United States.
With such a high risk of fatalities, establishing construction fall protection systems is a must. Not only is this a guaranteed way to safeguard workers and comply with the Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) regulations and health and safety standards. It also improves morale, leading to increased productivity and revenues.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
Who is Responsible for Fall Protection?
Regulations regarding working at heights and corresponding fall protection systems for construction are administered by specific agencies, depending on the region:
OSHA is the top federal agency enforcing fall protection rules in various sectors in the United States.
Safe Work Australia is the national policy body governing health and safety at work in Australia. Each territory in the country has regulators implementing the regulations.
Health and Safety Executive (HSE) is the national independent watchdog for work-related HSE issues in the United Kingdom.
The European Agency for Safety and Health at Work (EU-OSHA) provides guidance and information on fall protection. Each EU member state has an agency enforcing the rules.
The Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety is the government unit that establishes the rules under the labor code. Every province creates legislation and enforcement guidelines based on the federal ruling.
Companies should comply with these regulations, ascertaining that every member of their organization implements the following:
Employers are legally responsible for providing fall protection systems.
Health and safety managers develop, implement, and oversee the developed protocols.
Team supervisors (site managers) monitor their workers and ensure they are extensively trained in fall protection.
Workers should use the equipment provided and follow all safety protocols.
When is Fall Protection Required in the Construction Industry?
Fall protection in construction is mandatory. Here are some of the OSHA’s key guidelines:
The 6-foot Rule
This ruling states that fall protection is required when employees work at heights of six feet (two meters) above or below ground. In general industries (non-construction), the fall protection requirement is four feet or higher. In longshoring operations, the set height is eight feet.
Sites Requiring Construction Safety Fall Protection
According to the OSHA standard (1926.501), the following areas require fall protection:
Walking and working surfaces
Unprotected sides or edges
Ramps, runways, and walkways
Leading edges
Low slopes and steep roofs
Hoist areas
Holes and excavation sites
Scaffolds
Wall openings
Exceptions to Fall Protection
Personnel inspecting, investigating, and assessing workplace conditions before construction starts and after completion do not require fall protection in construction. However, fall protection is a must for the following:
Routine and frequent inspections
When there is a work pause due to equipment repairs or replacements
When the inspection work focuses on the fall protection system
To know more about the details, read the interpretation of OSHA fall protection in construction exceptions. It is also advisable to visit the websites of regulatory agencies in other countries to review their specific guidelines.
Essential Components of Fall Protection in Construction
There are several components in a fall protection system. These work together to protect workers from falling off heights and, in case an accident occurs, to minimize injuries.
Guardrails
These visible physical barriers are a primary measure that prevents workers from inadvertently stepping over edges. These are areas that require guardrails:
Around a balcony, ramp, or any elevated work surface
Around holes or any openings in floors and roofs
Around raised and open platforms and scaffolds
At the edges of catwalks and overhead conveyor platforms
Any place where workers could fall into water, hazardous substances, or operating machinery
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS)
PFAS is designed primarily to stop a worker from falling towards the lower floor or other objects in the event of a fall. It consists of several pieces:
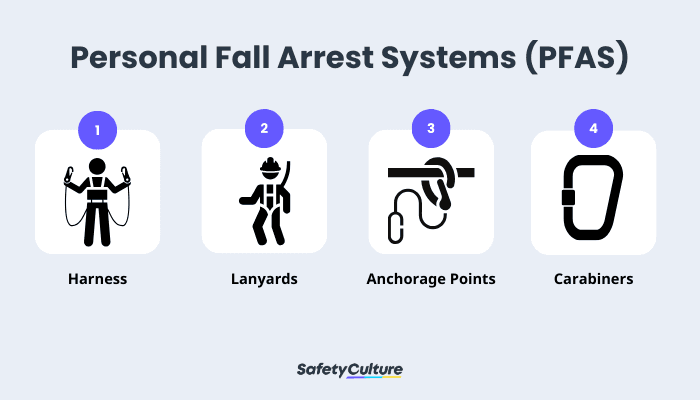
Personal Fall Arrest Systems (PFAS) for Construction Fall Protection
The harness , the wearable component of the PFAS, keeps the worker upright in case of a fall. It also ensures the force of the fall is evenly dispersed on the body and limits the maximum arresting force to 1,800 pounds.
Lanyards connect the harness to the anchorage point. High-quality ones have shock absorbers that reduce the force of the fall by slowing down the descent.
Anchorage points provide support for the PFAS. These are permanently attached to the structure where work happens.
Connecters and carabiners connect the lanyard to the harness and the harness to the anchorage point.
PFAS is different from a fall restraint system. The latter has a shorter lanyard that prevents workers from reaching zones where falls could occur.
Create your own Safety Harness Inspection Checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Safety Nets
This passive fall protection system, suspended below the work area, is designed to catch workers in case of a fall. Safety nets should be used with a PFAS to provide comprehensive protection.
Fall Prevention Training
Guardrails, PFAS, and safety nets are physical components that safeguard workers from falls. However, those would be substantially inadequate without OSHA-endorsed training and education. Here are some topics to include:
Purpose and use of fall arrest equipment
Hazard identification and assessment
Height requirements
Fall clearance calculations
Load testing
Emergency response protocols
Workers should be retrained when engineers, architects, and site managers make any change that affects the set-up of the fall protection system.
Protect Workers from Falls with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard. Efficiently manage and streamline health and safety processes across the organization, including incident management, safety audits and inspections, risk assessment, waste management, and more, using a comprehensive EHS software solution.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Environmental Safety
Safety

Oil Drum Storage: Safety Guide and Best Practices
Learn the practices for safe oil drum storage, its importance, and the regulations for compliance.
Environmental Safety
Safety

Flood Risk Management
Read this guide to flood risk management, its importance, and the key components and strategies for this process.
Environmental Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Stormwater Pollution Prevention Best Management Practices (SWPPP BMP)
Learn about the types of best management practices for SWPP and the steps to effectively implement them in prevention plans.