Achieving Compliance Objectives: Strategies for Success
Discover the importance of setting clear compliance objectives and understand how they enhance accountability and reduce risks in the organization.

Published 11 Feb 2025
Article by
7 min read
What are Compliance Objectives?
Compliance objectives are target goals organizations set to ensure adherence to laws, regulations, standards, and internal policies. Essential in industries with rigorous and constantly evolving rules, these objectives serve as a roadmap to minimize risk, safeguard stakeholders’ physical and data security, and protect the company’s reputation.
Importance
Organizations across industries face barriers in the continuously shifting corporate GRC and ESG requirements, making compliance management burdensome and almost impossible. Setting and working towards compliance objectives is an effective first step in this challenging endeavor and merits the following benefits:
Enhances risk management – By establishing objectives for compliance, organizations can target risk assessment and mitigation tasks and better prioritize resources to guarantee success. It’s particularly helpful in high-risk industries where non-compliance can result in hefty penalties per incident.
Improves operational efficiency – Companies can better streamline their processes when goals are well-defined and carefully mapped out. Compliance training, for instance, can be planned during goal setting and based on identified employee needs and forecasted emerging risks.
Boosts competitive edge – Integrating compliance objectives into the broader Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) framework ensures business sustainability, consequently building and strengthening trust among customers, suppliers, service providers, investors, and regulatory bodies.
Transform Your Compliance Strategy
Automate tracking and harness digital workflows to ensure compliance with evolving regulations effortlessly.
Types and Relevant Regulations
Compliance is more than just ticking off checkboxes to avoid expensive fines and legal issues. Every compliance objective serves a unique purpose: aligning operations with laws, protecting stakeholders, and maintaining standards. And all these are geared towards the company’s long-term success. Here are the different compliance objectives examples:
Legal
This compliance objective ensures adherence to regulations that govern the organization’s operations. It covers ongoing compliance monitoring in employment practices, consumer safety, and environmental protection, among others. Here are specific laws to take note of under this type:
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) is a US regulation preventing bribery in international business.
The Consumer Rights Directive (2011/83/EU) establishes fair contracts, transparent information before purchase, and the right of withdrawal or cancellation.
The Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Laws prohibit workplace discrimination based on race, gender, age, religion, or disability.
Financial
This goal focuses on meeting financial reporting standards, accounting guidelines, and tax laws, to name a few. It’s crucial for transparency,fraud prevention, and investor confidence.
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) mandates accurate financial reporting and auditing practices. It has become one of the most popular US federal financial laws as it increased transparency, accountability, and ethical standards.
Data Protection
This objective safeguards personal, customer, and employee data according to privacy laws and regulations. Prioritizing data protection compliance prevents data breaches that could expose customers’ personal information, financial data, and company secrets.
The European Union (EU)’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is one of the most rigorous data protection regulations. It applies to any organization processing personal information of EU residents, regardless of location.
Health & Safety
This compliance objective ensures that organizations promote employee well-being and protect workers from hazards. It involves creating safe work environments, reducing accidents, and holistically caring for their employees. There are several regulations to consider, depending on the location of operations:
Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) in the US
Canadian Center for Occupational Health and Safety (CCOHS) in Canada
Health and Safety Executive (HSE) in the United Kingdom
European Union Occupational Safety and Health Framework Directive (EU-OSHA)
Ethical
This establishes standards for fairness, transparency, and integrity beyond legal requirements. Ethical compliance objectives build a positive culture, boost employee morale, and foster public trust.
Although no global organization or regulatory body mandates ethical standards, many organizations across industries adopt the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics to promote integrity. Starbucks and Walmart are just a few global enterprises that make their codes of conduct publicly available.
How to Manage Compliance Objectives
Developing and maintaining compliance objectives requires collaboration among teams. A structured approach ensures that everyone understands the company’s goals, the key components, and the personnel’s roles in achieving them. Here are the steps organizations can take:
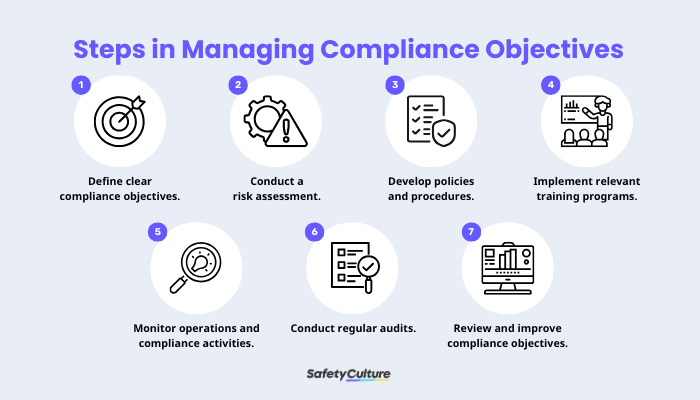
Steps in Managing Compliance Objectives
Step 1: Define clear objectives.
First, establish a foundation that outlines specific, measurable goals to help teams understand priorities and expectations. Compliance objectives should be based on current regulatory requirements, industry standards, and organizational values.
Step 2: Conduct a risk assessment.
Next, identify and evaluate potential compliance risks to determine appropriate mitigation strategies. When conducting risk assessments for compliance,prioritize the areas with the highest impact, focusing the resources on significant threats.
Here are tried and tested tools when assessing compliance-related risks:
Risk matrices visually represent the likelihood and impact of potential risks.
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) assesses the severity and plausibility of each failure mode.
Bow-tie analysis visualizes the sequence of events leading to a risk and its potential consequences.
Step 3: Develop policies and procedures.
Policies and procedures outline the specific actions to meet the established objectives successfully. These written documents guide employee behavior and ensure consistency across the organization.
Step 4: Implement relevant training programs.
Employees should understand their responsibilities regarding compliance objectives. Training programs raise awareness, build accountability, and empower employees to recognize and respond to compliance risks.
Here are some best practices to facilitate better learning during compliance training:
Tailor the program, basing it on specific roles, needs, and past performance of the employees.
Engage and motivate learners by using the most appropriate delivery method, such as online courses, group discussions, and role-playing exercises.
Conduct regular refresher training to reinforce key compliance concepts.
Step 5: Monitor operations and compliance activities.
Ongoing monitoring is essential to evaluate adherence to internal policies and government regulations. Compliance officers and relevant managers (e.g., legal, HR, IT, and security) can proactively identify and handle issues before they worsen.
Step 6: Conduct regular audits.
Perform compliance audits to assess the effectiveness of compliance programs,identify gaps or weaknesses in processes, and verify adherence to policies. Digital compliance audit checklists do more than simplify the task. It also helps schedule inspections, allows photo and video documentation, and upholds accountability with e-signatures and dedicated QR codes.
Step 7: Review and improve compliance objectives.
Continuous evaluation of compliance objects is crucial because there will always be changes in internal governance frameworks, operational practices, and external regulations. Adjustments should be made to ensure that the strategies developed based on the established goals remain effective.
How to Avoid Compliance Failures
The traditional approach to compliance, merely looking solely at rules and regulations and trying to tick as many as possible, is ineffective. Organizations should shift the focus to building a stronger culture of integrity, which starts with defining and setting compliance objectives well. Here are some specific ways to be on top of one’s compliance game:
Set clear, achievable objectives to provide clarity and direction. Poorly-defined goals can be vague and unrealistic, making implementation and evaluation difficult.
Leadership buy-in is vital. Secure support from the management (i.e., for funds, personnel, and tools) to implement compliance programs successfully.
Engage employees through open communication and ongoing training. When workers understand their roles and responsibilities, they will contribute to achieving compliance goals.
Set Clear Compliance Objectives with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries, such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline compliance workflows by automating tracking mechanisms and acquiring real-time insights for proactive monitoring and timely interventions. Simplify communication and documentation processes to disseminate expectations and meet regulatory deadlines. Foster a culture of accountability and transparency by empowering employees to take ownership of their compliance responsibilities through a unified platform.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Related articles
Operations
Business Processes

Implementing Value Management for Better Business Outcomes
Explore value management, its principles, benefits, and helpful strategies to drive peak performance and cost-efficiency.
Operations
Business Processes

A Guide to How Operations Automation Streamlines Workflows
Learn what operations automation is, which workflows require streamlining, and how it reduces errors to improve performance.
Business Processes
Operations

Yokoten: The Key to Quality Improvement
Get to know the basics of the Yokoten principle and how it accelerates continuous improvement by sharing known solutions across teams.