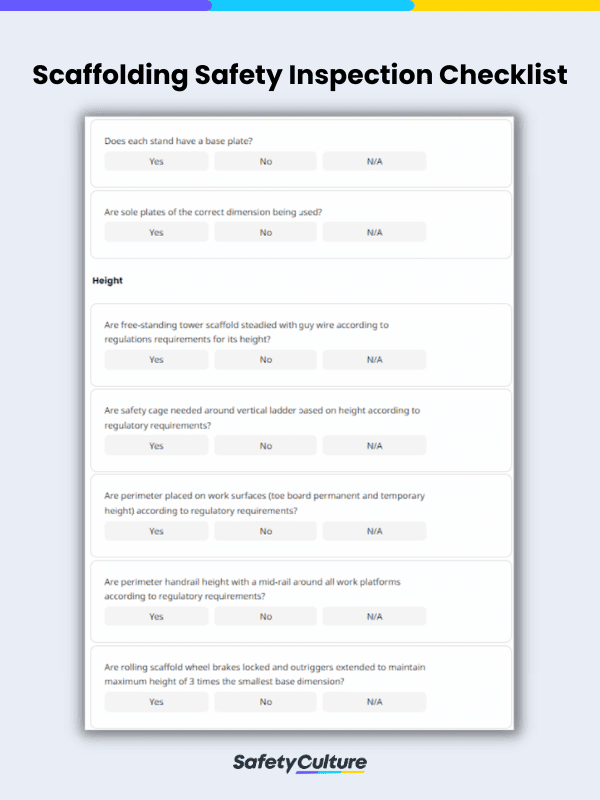
What is a Scaffold Inspection Checklist?
A scaffold inspection checklist is used to identify installation oversights and defects in scaffolding. These checklists should carry out critical and thorough evaluations focusing on a scaffold’s strength, rigidity, and stability, to ensure that it passes regulatory safety standards.
Why Conduct Scaffolding Inspections Using Checklists?
With the importance of scaffolding work in construction projects, erectors and users involved in scaffolding work must be protected through scaffolding safety inspections. Scaffolding safety inspections are important primarily because 65% of construction workers, or 2.3 million of them, frequently work on scaffolds according to the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Thorough scaffold inspections help spot both the apparent and underlying hazards that threaten the stability of the ground, scaffolding tower, and work structure, thus helping protect the livelihood of the workers involved.
With a dedicated scaffold inspection checklist, you can streamline your inspection process to save more time and money, as well as better improve the quality and safety of your workplace.
How do You Inspect Scaffolding?
Before using a scaffolding system, check that:
- Power lines near scaffolds are de-energized
- Scaffolds, tools, and materials are at least 10 feet away from energized power lines
- Scaffold is the correct type for the loads, materials, workers, and weather condition
- Footings are level, sound, rigid, and capable of supporting the loaded scaffold
- Legs, posts, frames, and uprights are on baseplates and mudsills
- Metal components don’t have bends, cracks, holes, and rust, among other things
- Scaffolds are in safe access. Do not use the cross braces as a ladder for access or exit.
- Wooden planks don’t have cracks, splits greater than 1 /4 inch, end splits that are long, many large loose knots, warps greater than 1 /4 inch, and other risky damages
- If the planks deflect 1 /60 of the span or 2 inches in a 10-foot wooden plank, the plank has been damaged and must not be used
- Planks are close together, with spaces no more than 1 inch around uprights
- 10-foot or shorter planks are 6 to 12 inches over the center line of the support, and that 10-foot or longer planks are no more than 18 inches over the end
- The platform is 14 inches or less from the wall, and 18 inches or less away if plastering/stucco.
- Guardrails and mid-rails on platforms where work is being done
- Workers under the platform are provided with protection. Make sure that hard hats are worn
- Braces, tie-ins, and guying are used as described by the scaffold’s manufacturer
General Scaffold Inspection Requirements
Generally, scaffold inspections must be performed in these three instances:
- after installation or assembly in any position;
- at least in intervals of 7 days thereafter; and
- after any circumstances that can jeopardize the safety of the scaffold.
Scaffolding inspection should be conducted by a scaffold competent person who possesses the minimum qualifications prescribed in their country of work. A final report must be provided by the assessor after each inspection.
US Scaffold Requirements
OSHA provides a comprehensive directive regarding the inspection of scaffolding used in construction work in the US. This includes the following guidelines:
- Have a competent person on site – A scaffold competent person must have sufficient training and experience to oversee the safe erection and use of scaffolding as defined by Appendix A in OSHA’s Inspection Procedures for Enforcing Subpart L, Scaffolds Used in Construction.
- Adhere to fall protection requirements – Fall protection is automatically required for employees working at a height of at least six feet or higher. Depending on the type of scaffold in use, employers may be required to provide a guard rail system, a personal fall arrest for each employee, or both.
- Check the scaffold’s rated load – The scaffold’s rated load refers to the amount of weight a scaffold is designed to carry. The maximum intended load refers to the total weight of the actual load you will put on the scaffold. As a safety measure, OSHA requires scaffolds to be capable of bearing four times the maximum intended load, not the rated load.
UK Scaffold Requirements
Similar to the US, the UK HSE also has specific requirements and guidelines on scaffold operation and use. For the most part, the standards are similar. Employers are legally required to examine risks and hazards before undertaking any scaffolding work, along with the following:
- Barrier use and status
- Scaffold design
- Types of scaffold to use
- Competence and supervision of scaffolding personnel
- Scaffold inspection procedures and documentation
Australia Scaffold Requirements
In Australia, licenses are required for work on scaffold platforms that have a potential fall of over 4 meters. These licenses are categorized as basic, intermediate, and advanced. For more information, refer to Safe Work Australia’s scaffolding safety guide.
The Working at Height Association (WAHA) has developed a scaffold safety inspection checklist that complies with these requirements.
Keep in mind that while various agencies govern these standards, they are globally recognized and adopted across different countries.
What to Include in a Scaffold Inspection Checklist
A typical scaffold inspection checklist will have fields for the following:
- Date and time of inspection
- Name of inspector and those involved
- Type of scaffold
- Description of work to be done with the scaffold
- Status and condition of scaffold base
- Presence of assistive wires, barricades, and railings for working at heights
- Symmetry and balance of equipment
- Size and condition of platforms and bracing equipment
- Condition of tubes and fittings
- Loading processes
- Presence and status of guard rails, toe boards, and tags
- Recommendations for next use and inspection
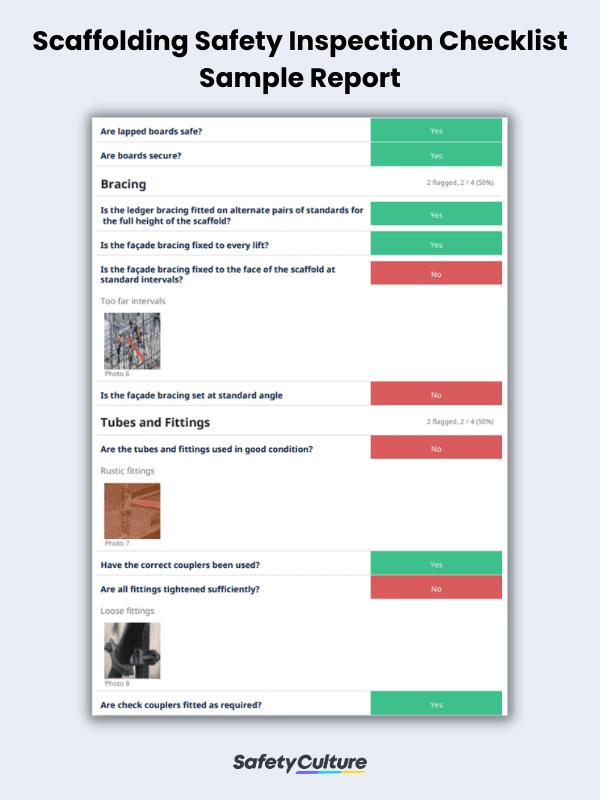
Here is a sample scaffold inspection checklist in use for reference:
FAQs about Scaffold Inspection Checklists
Ensure worker safety by following these 10 scaffolding safety tips:
- Provide proper training
- Ensure a stable foundation
- Provide guardrails and toe boards
- Conduct regular inspections
- Be aware of the weight capacity
- Ensure fall protection
- Consider the weather
- Provide proper access
- Keep the area clear
- Use checklists
Scaffolding tags are essential because they serve as warning devices for workers and other construction site personnel. Accidents, injuries, and other preventable incidents can be averted with the correct use of scaffolding tags.
While the US and UK have some of the most well-known and followed safety standards, other countries also have their own regulations to follow regarding scaffold safety. Some of the countries that have their own regulations regarding scaffold inspection and safety are: