Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is a Pool Inspection?
A pool inspection is conducted by a pool inspector to ensure that the entire pool system and its components are working properly. Additionally, pool inspections determine if the pool is in compliance with local safety regulations and requirements.
Why is it Important?
Pools aren’t a necessity but a luxury that adds value to a property or facility. This amenity can cost a lot to maintain and fix if any issue arises. One thing every homeowner or commercial property manager should do to keep pools ideal for use and leisure activities is to practice proper pool inspections and maintenance. Typically, pool inspections are conducted before the pool maintenance. Doing regular pool inspections can give visibility to any damages or issues on a pool equipment or component. This allows the inspector to report and send it for repair or maintenance.
It’s important to hire qualified pool inspectors. These pool inspectors underwent specific training for aquatic safety, they know the proper method of inspecting different types of pools, and would less likely miss any areas. Most local and state governments have resources online for the list of pool inspection requirements. Organizations such as the CDC, provided information about aquatic professionals, regulations, and pool codes. The Model Aquatic Health Code (MAHC) is an aquatic safety guide based on the latest technology and best practices. This also includes tools and training that could be utilized by pool inspectors and facility personnel.
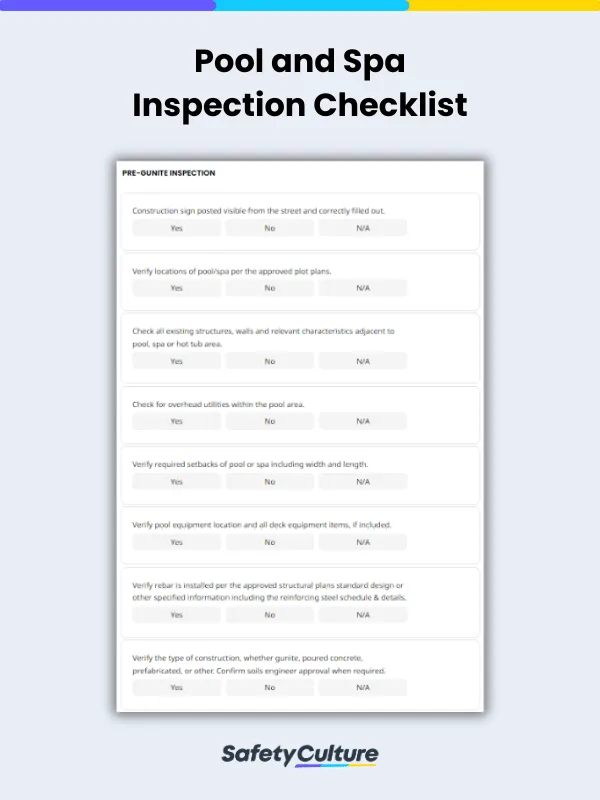
Homeowners and commercial property managers can download a copy of the applicable regulations file and use it as a checklist while supervising the pool inspector like this pool inspection checklist.
Different Types: Residential vs. Commercial
There are different types of pools made for residential and commercial use. These pool inspections will have different regulatory requirements to stay compliant with local and state regulations and codes. Aside from the regulatory differences, here are some general guidelines for a pool inspection per each type.
Residential
The International Association of Certified Home Inspectors (InterNACHI) provided the standards of practice for inspecting residential pools and spas. These standards are made up of non-invasive and visual examinations of the residential pool or spa to determine defects within the pool system or component. InterNACHI stated that the pool and spa inspection reports have to be noted down and pool inspectors can include the possible cause of the defect or issue. The standard of practice for a pool inspection is limited to technical aspects since aesthetic concerns aren’t required to be handled by an inspector.
Except in certain cases, most local and state governments don’t have regulations on residential pools and spas after it was built.
Commercial
Similar to residential pools, there are regulations and standards of practice for commercial pool inspections during construction. Numerous local government websites redirect the requirements of a pool inspection to the local health authority; however, they provide guidelines and sample documents of what to include during an inspection. Aquatic facility managers should check the guidelines posted by the local government to ensure compliance and avoid legal repercussions.
Different Areas To Examine
Pools and spas systems are made up of numerous components such as:
Filtration system and filters
Heater
Skimmer
Vents
Pressure gauge
Blower
Anti-drowning safety measures and barriers
Lights
Valves
Pumps and motors
With all these different components that make up the pool system, there are areas to look out for during a pool inspection:
5 Areas of a Pool Inspection
Safety features – during an inspection, pool inspectors should ensure that all safety features such as anti-drowning systems and barriers are working properly and in compliance with local regulations. Pool inspectors should be knowledgeable with the local codes since this could vary per location.
Physical condition – this includes, but is not limited to the plaster of the interior finish, pool tiles, and other materials. For saltwater pools, pool inspectors should check for any damages due to salt exposure.
Equipment – these are the parts of the pool system that keeps the pool working properly. It’s visible when there’s a defective component, for example a cloudy pool water can either be because of a damaged filtration system or a filter that needs to be replaced. Pool inspectors should inspect the equipment while the pool system is turned on or running and observe any visible or audible signs of damage.
Other additional features – these are the components that are customized to the specific pool such as an advanced purification system. Pool inspectors should ask the homeowner or commercial property manager for a list of components that were added to the pool to lessen the risk of missing out any area that could have defects during the inspection.
Equipment system and infrastructure condition – this includes the electrical system of the pool. Pool inspectors can inspect the breaker if it’s functioning properly and also for possible grounding and leaks. Additionally, pool inspections need to consider infrastructure conditions such as the drainage system. A proper drainage system helps efficiently drain the pool and be refilled with fresh water. This allows people to have continuous and stress-free swimming enjoyment.
What Should be Included in a Pool Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pool inspection checklist should cover safety, structural integrity, equipment functionality, water quality, and compliance with local regulations. Below are the main key components to consider in the checklist:
Physical Condition
Pool shell and coping: Inspect for cracks, discoloration, pitting, or open joints that could indicate leaks or deterioration.
Decking: Check for slip resistance, separation from pool wall, standing water, and trip hazards.
Tiles and interior finish: Look for damage, missing tiles, or signs of salt exposure in saltwater pools.
Safety Features
Fencing, gates, and screen enclosures: Ensure barriers meet local safety codes, are self-closing, self-latching, and gates open outward from the pool area.
Anti-drowning systems: Check for compliant drain covers, pool alarms, and pool covers.
Proper signage: Ensure required safety and depth signs are visible.
Equipment and Systems
Filtration system: Assess filters, pumps, skimmers, blowers, and pressure gauges for proper operation and leaks.
Heaters: Ensure heaters function correctly and are free from leaks or corrosion.
Lighting: Verify pool light fixtures are securely attached, properly grounded, and protected by GFCIs.
Electrical system: Check breaker, wiring, bonding, and grounding of all equipment; ensure compliance with electrical codes.
Plumbing: Inspect pipes for leaks, proper pressure, and clearance from roots or debris.
Drains: Confirm anti-vortex covers are present, secure, and compliant with regulations.
Water Quality and Chemistry
Water clarity: Ensure water is clean, clear, and free of debris.
Chemical levels: Test for appropriate chlorine/bromine, pH, and other required chemical balances.
Additional Features and Infrastructure
Customized systems: Inspect any advanced purification or automation systems unique to the pool.
Drainage: Verify proper drainage around the pool to prevent standing water and structural issues.
Pool/spa covers: Ensure covers are compliant and in good condition.
Documentation and Compliance
Verify pool placement, setbacks, and proximity to utilities and structures.
Check for required approvals, permits, and compliance with local building codes
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.