Published 26 Sept 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is an Internal Control Checklist?
An internal control checklist is a systematic tool used by organizations across industries to assess the effectiveness of their internal control systems. It serves as a framework for evaluating whether existing policies and procedures align with the organization’s objectives by identifying areas of potential risk or inefficiency. This checklist, designed to promote transparency and accountability, typically includes sections on risk management, financial oversight, regulatory compliance, and operational safeguards.
Benefits of Implementing an Internal Control Checklist
A checklist for evaluating internal controls offers significant advantages that enhance organizational efficiency, compliance, and security. Here are the key benefits of effectively using one:
Improved risk management – An internal control checklist template helps identify potential risks in financial reporting, operational processes, and compliance areas. By proactively addressing these risks, organizations can prevent fraud, errors, and inefficiencies before they escalate. This systematic approach to risk management ensures business continuity and strengthens decision-making processes.
Enhanced accuracy in financial reporting – Using a checklist ensures all financial transactions and reports comply with established standards and regulations . This reduces errors and discrepancies in financial data and enables organizations to present reliable and transparent records. Accurate financial reporting builds stakeholder trust and supports better strategic planning.
Strengthened compliance management – This checklist ensures that the organization adheres to relevant industry regulations and internal policies . By regularly reviewing compliance measures, businesses can avoid costly penalties and maintain a good standing with regulatory bodies.
Increased operational efficiency – An internal control self-assessment checklist streamlines processes by standardizing workflows and eliminating redundancies. This improves productivity across departments while maintaining good resource management . Enhanced efficiency also reduces costs, allowing organizations to allocate resources to growth initiatives.
Maintained stakeholder confidence – Organizations that implement internal control checklists exhibit strong governance practices , which appeal to investors, customers, and partners. Demonstrating accountability and transparency fosters long-term relationships and positions the company as a trustworthy entity in its market.
What to Include in an Internal Control Self Assessment Checklist
For businesses of all sizes, leveraging an internal control checklist is a proactive step toward fostering operational efficiency and mitigating risks in a structured and consistent manner. Fundamentally, an internal audit control checklist covers the following components:
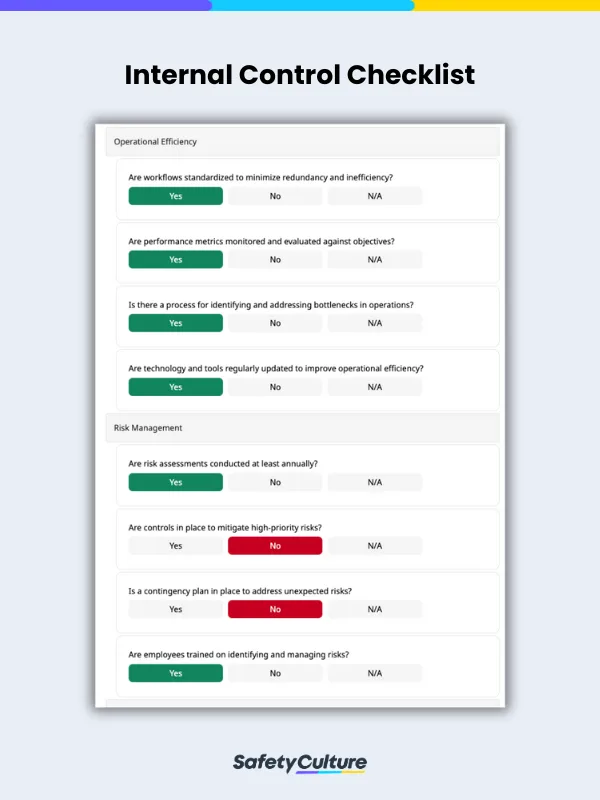
Governance and leadership
Financial reporting and accuracy
Operational efficiency
Risk management
Compliance and regulatory adherence
IT security and controls
To see how these components look like in the checklist, here’s a filled-out internal control sample report:
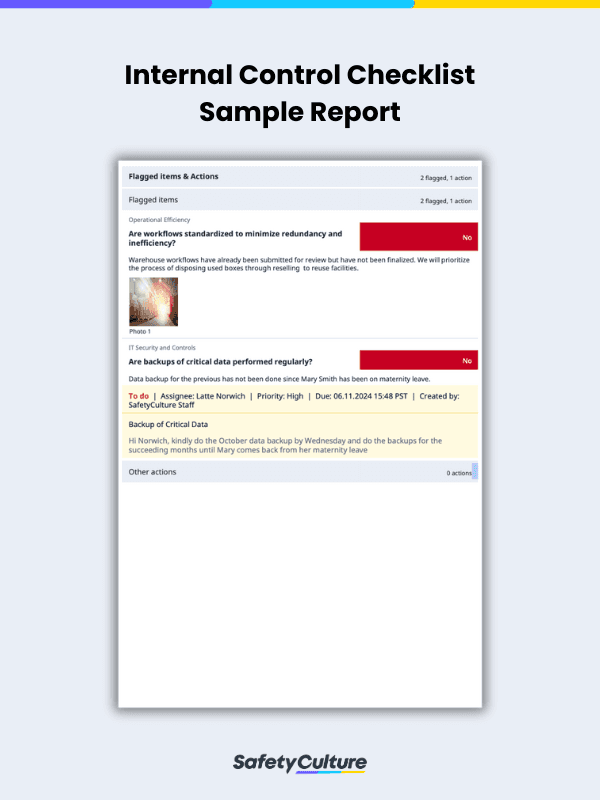
Internal Control Checklist | SafetyCulture
How to Strengthen Internal Controls Using a Checklist
By following an internal control checklist, organizations can systematically evaluate and enhance their processes. Here’s a detailed guide to help organizations use this tool effectively:
1. Align objectives with organizational goals.
Define the purpose of internal controls in line with the organization’s overall objectives. Clearly outline what you aim to achieve, whether it’s improving financial reporting accuracy, ensuring regulatory compliance, or safeguarding assets. Establish the scope of the checklist to address specific areas like risk management, operations, or cyber security because clear alignment ensures that the internal control checklist will drive meaningful improvements.
2. Develop a comprehensive internal control checklist.
Internal auditors can take the lead in designing or updating the checklist, incorporating input from all relevant departments. The checklist should include categories like financial oversight, compliance measures, risk management, and operational safeguards. Tailoring the checklist to address specific organizational needs ensures a holistic evaluation. Use industry best practices or regulatory requirements as a reference to ensure your checklist is comprehensive and relevant.
3. Promote interdepartmental collaboration and assign responsibilities.
Foster collaboration between departments to encourage active participation in internal control assessments. Designate team members or departments responsible for completing sections of the checklist.
Finance managers, operations managers, and risk managers can coordinate to ensure all aspects of the checklist are reviewed and addressed thoroughly because a unified approach improves consistency and accountability.
Clear accountability also ensures each area is thoroughly reviewed and no critical aspect is overlooked. Bear in mind that training employees on the purpose of the checklist can further enhance its effectiveness.
4. Conduct regular assessments.
Use the checklist to perform routine evaluations of internal controls. Check each aspect or process systematically, document findings, and highlight gaps or weaknesses. Regular assessments enable the organization to monitor progress and quickly address emerging risks or inefficiencies.
5. Implement necessary improvements.
Based on the assessment results, compliance officers and operations managers can implement necessary improvements, such as policy updates or new training programs. Finance managers can oversee changes in financial procedures to ensure accuracy and compliance. Swift corrective actions strengthen internal control frameworks and reduce vulnerabilities.
6. Monitor and update the checklist.
Internal auditors and risk managers should continuously monitor the effectiveness of implemented changes. Use these insights to make strategic decisions and ensure the checklist remains relevant. Regular updates incorporating emerging risks and new regulations prepare the organization for future challenges.
7. Communicate results and foster accountability.
Set the tone for accountability and encourage employees at all levels to engage with internal controls actively. Transparent communication about checklist findings and improvements builds trust and reinforces a culture of compliance and risk awareness across the organization. Use a trustworthy internal control software to make this process more efficient.
Still looking for a checklist?
Search, filter, and customize 60,000+ templates across industries and use cases.