What is a Risk Control matrix?
A risk control matrix is a structured tool for identifying, assessing, and managing risks within an organization’s processes or operations. It serves as a comprehensive framework that maps risks to corresponding controls, ensuring that all potential vulnerabilities are addressed effectively.
By providing a clear and organized overview, the risk control matrix plays a critical role in risk management, internal audits, and compliance with regulatory standards. This tool is especially valuable in industries where mitigating financial, operational, or cyber security risks is essential to sustaining business continuity and safeguarding stakeholder trust.
What is a Risk Control Matrix Used For?
Implementing a risk control matrix offers a wide range of benefits that help organizations strengthen their risk management, compliance, and operational processes. Below are the key advantages:
- Enhanced risk identification and mitigation – A risk control matrix provides a systematic approach to identifying and addressing risks in organizational processes. Mapping specific risks to corresponding controls ensures that all potential vulnerabilities are accounted for and mitigated. This proactive framework reduces the likelihood of financial losses, reputational damage, or regulatory penalties.
- Streamlined decision-making – With a clear and concise overview of risks and controls, the risk control matrix empowers decision-makers to prioritize risk mitigation efforts while ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to address the most critical risks. This supports informed decision-making and promotes operational resilience in an ever-changing risk landscape.
- Ongoing risk monitoring and adaptability – An internal control risk assessment matrix evolves alongside an organization’s operations and external environment. Regular matrix updates enable organizations to adapt to emerging risks and shifting business priorities, ensuring risk management efforts remain relevant and effective over time.
Take Control of Your Risk Landscape
How to Prepare Risk Control Matrix?
Creating a risk control matrix involves a structured process that ensures all potential risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated effectively. Follow these steps to prepare a comprehensive risk control matrix:
1. Define the scope and objectives.
Start by determining the scope of the risk control matrix. Specify the processes or projects you want to evaluate. Define clear objectives, such as compliance with regulations, enhancing operational efficiency, or mitigating specific risks. This primary step ensures the matrix is aligned with organizational goals.
2. Identify key risks.
List all possible risks related to the established scope. Consider financial, operational, regulatory, cyber security, and reputational risks. Engage stakeholders and review historical data or risk assessments to ensure comprehensive risk identification. Group similar risks to maintain clarity and focus.
3. Set control objectives.
For each identified risk, establish a control objective that specifies the desired outcome. Control objectives should align with your organization’s policies and industry standards. For example, a control objective for cyber security risks can be “Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.”
4. Define control activities.
Identify specific actions or processes that address each control objective. These are the measures or practices implemented to mitigate risks, such as implementing access controls, conducting regular audits, or training employees. Each control activity should be actionable, measurable, and linked to the corresponding risk.
5. Assign risk owners.
Assign responsibility for each risk and control to specific individuals or teams. Risk owners are accountable for monitoring, implementing, and ensuring the effectiveness of the assigned controls. Clear ownership fosters accountability and ensures timely action.
6. Evaluate risk severity and control effectiveness.
Assess the likelihood and impact of each risk along with the effectiveness of the corresponding controls. Use a standardized rating system, such as high, medium, or low, to prioritize risks and focus efforts on the most critical areas.
7. Document and organize the matrix.
Compile the information into a structured matrix format. Typically, columns in the matrix include the following:
- Risk description
- Control objective
- Control activities
- Risk owner
- Risk severity (likelihood/impact)
- Control effectiveness rating
Ensure the matrix is clear, concise, and accessible to all relevant stakeholders. To see how these elements play out, here’s a filled-out risk control matrix sample:
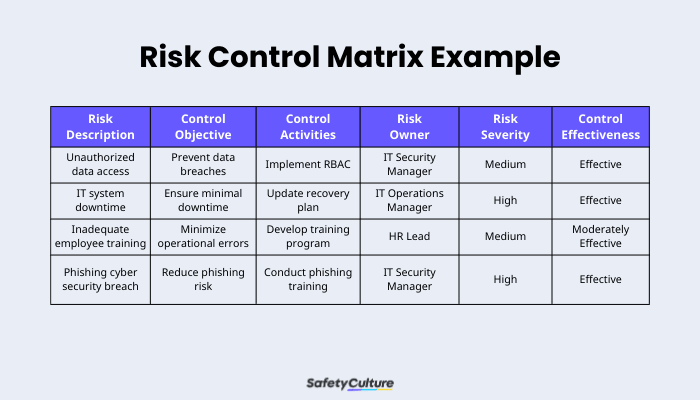
Risk Control Matrix Example
8. Review and update regularly.
A risk control matrix is a dynamic document that requires regular updates. Review it periodically to account for new risks, changes in operations, or updates to regulations. It’s also important to engage stakeholders in these reviews to maintain accuracy and relevance.



