Unlock hidden efficiency
Middle managers lose over 5 hours each week on low-value tasks—time that could be spent driving meaningful progress. Learn why they hold the key to operational success.

Learn about what PFMEA is and how it is performed to prevent process failures

Published 23 Aug 2024
Article by
7 min read
Process Failure Mode Effects Analysis (PFMEA) is a qualitative tool designed to prevent failures in operations. Also called Process FMEA, it supports initiatives for improvement by identifying and analyzing potential failures within a process. PFMEA is derived from the broader FMEA method and is typically used across various industries to enhance productivity and improve quality.
Conducting PFMEA allows teams to prepare and build process safeguards that’ll reduce or prevent the occurrence of operational downtime, injury or accident, costly repairs, and reworks in the business.
PFMEA is conducted when the following occurs in the organization:
New changes are made on existing processes
New technology, equipment, or process steps are being introduced
Implementing a process to a new facility, or department
Integrating PFMEA in process improvement initiatives offers several advantages, including:
Prevention of failure – : PFMEA helps identify potential failures before they happen, allowing organizations to take proactive measures to minimize their occurrence, if not eliminate them.
Improved process reliability -Promoting process correction, prevention, or redesign allows organizations to monitor critical parameters and develop effective control plans. This leads to enhanced process efficiency and reduced waste.
Enhanced quality – By focusing on preventing process-related issues, PFMEA leads to higher product and service quality, reducing defects and rework.
Cost savings – Preventing failures and improving process efficiency can significantly reduce costs associated with downtime, scrap, rework, and warranty claims.
Increased customer satisfaction – Delivering higher quality products and services with fewer defects increases customer satisfaction and trust.
Unlock hidden efficiency
Middle managers lose over 5 hours each week on low-value tasks—time that could be spent driving meaningful progress. Learn why they hold the key to operational success.

Conducting Process FMEA can be summarized into 7 steps, which are as follows:
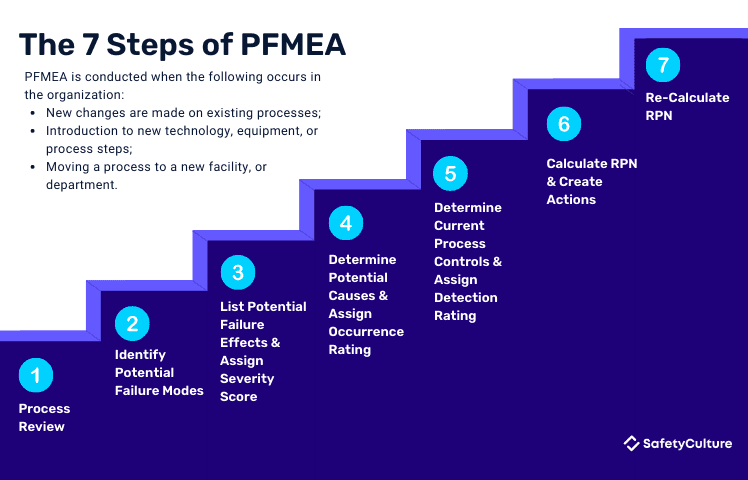
When starting PFMEA, it is important to first determine the focus of your evaluation. Is it a business process? A service process? Or a production process? Once you’ve determined what area you want to focus on, start reviewing the steps associated with it and determine what each step intends to accomplish. One of the best ways to do this is putting it on a flowchart for better visualization.
What could possibly go wrong in the step? Potential failure modes are scenarios that may derail the process from the intended outcome. For example, in a manufacturing company, it is quite common to use machineries like pallet conveyors for moving products as part of the production process. A potential failure mode for that process could be that boxes or bottles may slip, dash, or get damaged as they travel along the conveyor.
What could be the result if the identified potential failure occurs? Consider its impact on the customers, workers (e.g. injury), environment, facility, and even the process itself. There may be more than one, so list them all down and try to be as detailed as possible. When that’s done, rate its severity with 1 being the lowest and 10 as the highest. Severity ratings are based on how serious the consequences are.
What could trigger the potential failure mode? Determine the possible causes and trigger(s) for the failure mode effect to occur. For example, using the same situation mentioned in step 2. If an employee injury occurs due to the identified failure mode, how might that occur? Is it because the employees weren’t wearing the appropriate PPE or is it due to machinery malfunction? Once that’s determined, assign the appropriate rating for occurrence with 1 being the lowest and 10 as the highest. Occurrence ratings are based on how frequently the trigger or cause is likely to occur.
Are there existing controls that prevent or detect the failure mode from occurring? Ideally, process steps will have safeguards in place. Write down any related controls and assign detection rating to each, with 1 being the lowest and 10 as the highest. Detection ratings are based on how easily the failure mode will be detected using the current controls.
In calculating RPN, a process is evaluated and assigned a score on a scale of 1 – 10 and then multiplied to each other. The Risk Priority Number (RPN) will help determine teams which risks to prioritize and create corrective actions. Should the failure mode result in a high RPN, an action plan is created for either corrective measures or improvements. The action plan consists of a detailed instruction or lists of steps to take, assigned personnel to do them, and the target date of when it should be completed.

After the completion of the action plan, the PFMEA should be re-evaluated by re-calculating the RPN to measure its impact.
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
To better understand the steps of conducting PFMEA, below is an example that illustrates the PFMEA process in action in the manufacturing industry.
In this example, a food manufacturing company evaluates the process steps in the production of their food products. All steps associated with the process are then listed down. For this example, we’ll focus on one process step:
Process step, variable, or key input:Loading products into the machinery line/production line |
Using this process step, the next actions involve: identifying potential failure modes, listing potential failure effects, assigning severity score, determining potential causes, assigning occurrence rating, determining current process controls, and assigning detection rating. Below is a table depicting all these actions:
Process step, variable, or key input: | Potential Failure Mode | Potential Effect on Customer/Workers Because of Defect | *SEV | Potential Causes | *OCC | Current Process Controls | *DET |
Loading products into the machinery line/production line | boxes or bottles may slip, dash, or get damaged as they travel along the conveyor | This will delay reaching our production quota which can affect our delivery schedules. It can also cause injuries to workers and damage to facility equipment. | 6 | Machinery malfunction, Operating machinery in the wrong settings | 4 | Pre-operation checks on machines, Proper PPE for employees, Regular maintenance schedule for machineries, Training certifications for employees responsible for operating machineries. | 8 |
*SEV – severity score; OCC – occurrence rating; DET – detection rating.
Once all this information is laid out, RPN is then calculated for all the process steps to determine which are the most pressing risks to address. For failure modes resulting in a high RPN, an action plan is devised consisting of detailed instructions or lists of steps for either corrective or improvement purposes. Later on, the RPN is re-calculated to measure the impact of the implemented action plan.
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Processes are a set of actions and steps taken in order to achieve the desired result. It serves as our foundation in all the things we do to achieve our goals. Processes ensure that all steps and actions taken are done in the right way and right time, making it easy to navigate towards the desired outcome. Moreover, it also affects the safety and quality of products and the people involved in it.
In a 2019 industry profile in the United States, the manufacturing industry was considered as one of the top 10 dangerous industries. Injuries and accidents reported commonly occur in the production process. In another report from HSE, statistics showed that most of the injuries in manufacturing are caused by coming into contact with objects or machinery, and slip, trip, or fall.
These reports prove just how critical it is for industries to be conscious of the processes they’ve laid down. To prevent business mishaps and to protect workers, processes should be guided by industry standards and best practices. Organizations can also create their own standards and best practices based on their own evaluation and analysis of processes through use of tools like PFMEA.
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs ✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents ✓ Boost productivity and efficiency ✓ Enhance communication and collaboration ✓ Discover improvement opportunities ✓ Make data-driven business decisions
Digital Tool
Operations

Learn about the types of forms your business can use to standardize processes, collect valuable and actionable data, and ensure compliance.
Logistics
Operations

Understand warehousing logistics and manage the storage, movement, and handling of inventory to effectively meet supply and demand.
Operations
Human Resources

Learn what an HR health and safety program covers, its key responsibilities, and the best practices for creating safer working environments.