What is a BSCI Audit?
A Business Social Compliance Initiative (BSCI) audit is the process of assessing an organization’s social compliance in the global supply chain. It aims to evaluate the processes and working conditions of the organization if it adheres to the principles of the BSCI code of conduct. A BSCI audit is essential to create a consistent and harmonious ethical supply chain.
Importance of BSCI Audit
Conducting a BSCI audit helps the organization in monitoring and assessing workplace standards including traders, vendors, and suppliers if they demonstrate social responsibility across the global supply chain. It helps the organization to:
- avoid labour issues of their suppliers;
- standardize policies and processes according to the global market trade; and
- reduce unnecessary damage costs and negative press.
11 Principles of Business Social Compliance Initiative Code of Conduct
BSCI was established in 2003 by the Foreign Trade Association (FTA) to establish a common platform for the various European companies’ codes of conduct and monitoring systems. The following are the principles observed under BSCI code of conduct:
- The Right of Freedom of Association and Collective Bargaining
Employees have the right to join or form a union group to cooperate and engage in a dialogue about workplace issues and collective bargaining. - Fair Remuneration
Employees should receive fair compensation for the service they provided. It should be sufficient to provide them with a decent living for themselves and their families. - Occupational Health and Safety
The organization must comply with Workplace Health and Safety (WHS) practices implemented and followed across the business. Partners should protect their employees in any work-related incidents, injuries, and illnesses. - Special Protection for Young Workers
Business partners should ensure the health and safety of young workers considering the kind of work, health risks, and working hours which would likely affect their attendance and participation at school. - No Bonded Labour
Business partners shall not participate in any form of servitude or non-voluntary labour. They should allow their workers the right to leave work and terminate their employment provided with reasonable notice to their employer. - Ethical Business Behaviour
The organization should observe the principle of a corruption-free environment. Transparency is observed in all activities involving structure, training, and employee performances. All data information should be reliable and accurately recorded. - No Discrimination
The organization shall not discriminate, exclude or have a certain preference for choosing their employees on the basis of disabilities, race, gender, and more. - Decent Working Hours
Employees are not required to work more than 48 regular hours per week, without prejudice to specific expectations. In exceptional cases defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) overtime may be permitted but it should be voluntary, doesn’t compromise Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs), and paid at a premium rate of not less than one and one-quarter times the regular rate. - No Child Labour
The organization should establish a clear policy in employing their workers. Upon recruitment employers shall ensure the applicant is not less than 15 years of age unless the job is under the exception recognized by the ILO. - No Precarious Employment
Employers should secure a written contract for all onboarding employees covering the national legislation, custom or practice, and international labour standards. - Protection of the Environment
The organization should assess the environmental impact of operations including waste management, and establish effective policies and procedures to protect the environment, community, and natural resources.
3 Practical Steps to Prepare for BSCI Audit
Preparing the organization for the BSCI audit secures employees and business compliance with social responsibility in the global trade market. Below are practical steps to prepare for BSCI audits.
- Be familiar with the BSCI Code of Conduct
The organization must be conversant about the clause and content of the principles of the BSCI Code of Conduct to ensure it was regulated properly within the organization. - Conduct an internal audit
Performing BSCI internal audits could help the organization prepare for the actual audit. An initial assessment of policies and regulations help identify organizations’ non-compliance with regulatory standards. Also, it helps determine employee gaps and improvement needs immediately. - Use a BSCI audit checklist
The checklist is used by auditors to guide them in evaluating the condition, policies, and regulations of an organization to ensure it enforces the principles of the BSCI code of conduct.
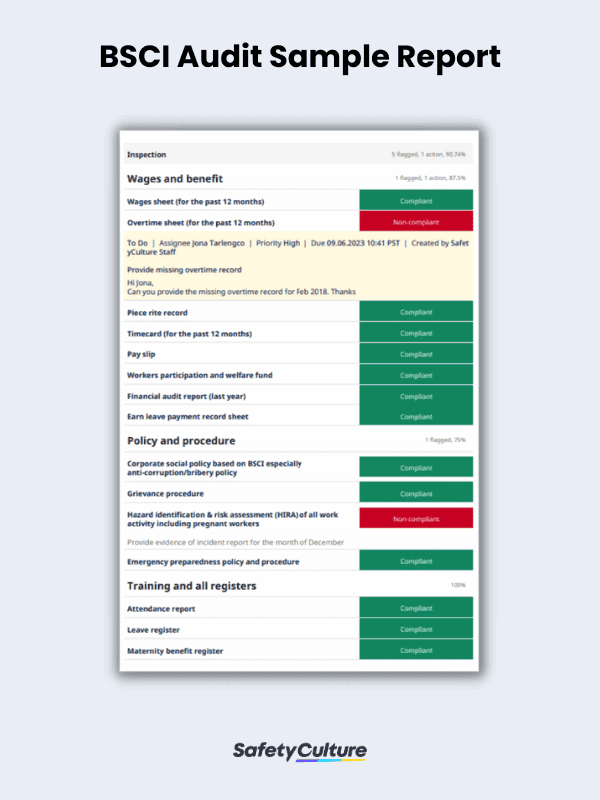
BSCI Audit Sample Report | SafetyCulture