The Meatpacking Industry: How Meat Reaches the Market Safely
Learn how meatpacking plants operate and discover the technologies improving efficiency, safety, and traceability.

Published 23 Dec 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is Meatpacking?
Meatpacking is the highly regulated industrial process of converting livestock into market-ready meat products. It involves the hygienic slaughter, processing, fabrication, and packaging of beef, pork, or poultry. By following a strict food safety framework, producers can ensure safety and traceability when distributing to consumers, restaurants, and other retailers.
Importance of Hygienic Meatpacking
Meatpacking is a foundational step within the broader meat processing sector. The entire industry was transformed during the 19th century, with the emergence of railroads, mechanization, and eventual adoption of refrigeration. Today, simple farm slaughter has become highly structured and regulated to ensure the following:
Prevent food-borne illnesses : Poor hygiene practices can lead to the spread of pathogens like Salmonella, E.coli, and Listeria. Ingesting these can cause serious health issues.
Protect worker health and safety : Butchers and meat packers face significant occupational risks, from biological hazards to environmental stressors. Maintaining clean and sanitized facilities and following food safety guidelines mitigate their exposure.
Avoid recalls and associated legal issues : Hygiene failures risk widespread recalls and millions in liability and lost business. Investing in rigorous cleanliness is always cheaper than managing contamination fallout.
Ensure supply chain stability : Disruptions due to hygiene or health issues, such as facility shutdowns from health outbreaks , can affect supply. Keeping conditions sanitary prevents any of these compounding problems.
Extend shelf life and reduce waste : Early contamination accelerates spoilage and limits storage life. On top of upholding public health, safe food practices like proper refrigeration maintain a reliable food supply.
Explore SafetyCulture Monitoring Solution
Utilize advanced sensor technology to monitor assets, automate vital alerts, implement actions, and report urgent issues.
Key Components and How the Process Works
The meatpacking industry consolidated rapidly from the 1970s. For example, there are only four big firms controlling the majority of beef in the US in 2025. While this lowered processing costs, it also increased worker hazards and related supply fragility. This directly led to the creation of safe procedural components that now fundamentally shape the entire meatpacking process.
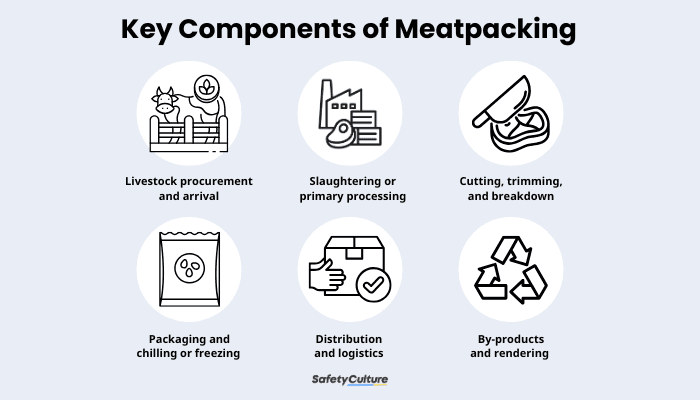
Key Components of Meatpacking
Here are the key components and processes of meatpacking:
Livestock procurement and arrival
The first step involves buying animals from farms, inspecting their health during transit and upon reaching the plant, and providing resting time. Traceability, welfare compliance, and detailed documentation are mandatory requirements throughout this phase. This is because animal stress can lead to injuries, low quality meat, and higher microbial load.
Slaughtering or primary processing
Animals should be humanely stunned, slaughtered, and washed. Carcasses are then promptly transferred to cold, controlled areas because they are highly susceptible to microbial contamination at this point. Government inspectors typically perform checks at this stage, focusing on:
Strict sanitation SOPs
Separate clean from dirty zones
Validated evisceration procedures
Knife sterilization
Consistent carcass washing
Cutting, trimming, and breakdown
Carcasses are moved from the initial chilling phase and broken down into various components (e.g., primal, subprimal, and retail cuts). Specialized workers debone, trim excess fat, remove defects, and prepare the final meat products for packaging or further processing.
Cross-contamination must be a priority check at this point because there are numerous opportunities for pathogens to spread. Workers are also at heightened risk because of their tools, such as knives, saws, and processing machinery.
Packaging and chilling or freezing
At this point, meat is vacuum-sealed, placed in bulk packaging, and rapidly child or frozen to inhibit microbial growth. Labels are added for traceability. Cold chain monitoring and continuous temperature logging is vital to prevent rapid bacterial growth, which could cause spoilage and subsequent health outbreaks.
Distribution and logistics
Finished meat products are loaded onto refrigerated trucks, stored in cold warehouses, and delivered to retailers, processors, restaurants, or export facilities. The integrity of the cold chain is highly vulnerable during transport, making continuous temperature verification and strategic route optimization mandatory to prevent spoilage and maintain safety until the product reaches its final recipient.
By-products and rendering
During processing, all non-meat components (such as fat, bones, organs, and hides) are systematically collected. These materials are then utilized to create co-products like tallow, pet food, fertilizer, and pharmaceutical ingredients.
Although this is not part of the traditional meatpacking procedure, modern companies include co-product utilization to minimize waste, maximize plant efficiency, and drive sustainability goals.
Create your own Food Safety checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Regulatory and Safety Requirements
Consumers expect final products to reflect high safety, ethical, and hygienic standards throughout the entire supply chain. Get to know the global meatpacking regulations that protect public health by maintaining safety from farm to consumer:
Codex Alimentarius Code of Hygienic Practice for Meat: Set by the Food and Agriculture Organization and the World Health Organization, this set benchmarks for slaughter hygiene, facility design, and microbiological criteria, among others.
ISO 22000 : This integrates Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), prerequisite programs, and risk management for food safety. Documentation is crucial under this global standard.
OIE Terrestrial Animal Health Code: This sets standards for humane handling, transport, stunning, and slaughter processes. It ensures meatpacking facilities minimize animal stress, contamination risk, and injuries.
Food Safety and Inspection Services (FSIS): The US Department of Agriculture enforces rules for sanitary slaughter and processing of animals, as well as labeling, careful distribution, and continuous inspection. The UK’s Food Standards Agency (FSA) and Australia’s Department of Agriculture, Fisheries, and Forestry (DAFF) have the same mandate.
Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): The US Food and Drug Administration mandates preventive controls, allergen management, and traceability. The UK’s Food Safety Act (FSA) and Australia’s Food Standards Code (FSANZ) have similar rules.
How Tech Helps
In a multibillion-dollar industry that employs hundreds of thousands of workers, technology boosts efficiency and output, reduces waste, and enhances safety for frontline meatpackers. Here are some essential tools that companies, big and small, can leverage to gain significant, competitive benefits.
Digital checklists : Every line can follow the same procedure, from pre-operation hygiene checks to equipment maintenance, reducing human error and supporting HACCP compliance.
Issue reporting : Strengthen food safety by catching problems at the point of detection by enabling workers to report hazards, contamination risks, equipment failures, or animal welfare concerns.
Digital records: Improve traceability by storing temperature logs, inspection data, and production checks with timestamps and photo evidence.
Centralized documentatio : Ensure staff can always access up-to-date procedures with easy-to-access SOPs, HACCP plans, MSDS sheets, sanitation procedures, and audit requirements in one secure digital library.
Smart analytics: Make data-driven decisions by converting inspections and reports into dashboards that show trends, compliance gaps, and high-risk areas.
Training Improve worker competency and preparedness, and reduce safety incidents by delivering microlearning training, tracking employee certifications, and assigning refresher modules for food handling hygiene, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), animal handling, and sanitation.
Integration : Create a seamless digital ecosystem by syncing the company’s other systems such as manufacturing resource tools and asset management systems into one platform, providing a unified view of food safety, operations, and compliance across all plants.
Enhance Safety and Quality in Meatpacking with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Meatpacking
Related articles
Operations
Business Processes

Mastering Workflow Orchestration for Operational Excellence
Learn everything about workflow orchestration, its benefits, common tools, and best practices for efficient enterprise process management.
Operations
Performance Evaluation

Conducting Business Health Checks for Long-Term Success
Learn what a business check is, its benefits, and how to conduct one effectively. Discover key components and relevant laws for your region.
Operations
Business Processes

Implementing Value Management for Better Business Outcomes
Explore value management, its principles, benefits, and helpful strategies to drive peak performance and cost-efficiency.