Process Equipment in Modern Industrial Systems
Explore the role of process equipment in industrial processes, from core components to design, operation, and maintenance.

Published 27 Jan 2026
Article by
7 min read
What is Process Equipment?
Process equipment refers to specialized machines and devices used to carry out chemical and materials processing. This kind of equipment includes mechanical and engineered systems that facilitate physical and chemical transformations, such as compressors, separation units, pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and reactors. These should meet operational, safety, and regulatory requirements to ensure efficiency across production environments.
The Critical Role of Process Equipment
As industries evolved from manual labor to mechanized production, processing equipment transformed the industry by automating tasks, which improved product consistency and manufacturing safety. From basic processing, such as food preservation, handstitching garments, or assembly by hand, advanced tools made operations faster and more reliable across industrial environments.
In the modern industrial landscape, process equipment is no longer just a functional requirement. It is a primary driver of competitive advantage. World-class facilities are defined by the precision of their equipment, ensuring chemical and mechanical compatibility, continuous uptime, and energy efficiency.
Manage Factory Assets with Confidence
Maximize equipment uptime with real-time asset visibility and automated preventive maintenance workflows.
What are the Common Types of Process Equipment Across Industries?
Manufacturing process equipment serves different purposes, from material transformation to heat, mass, and fluid transfer. Because each process has unique operational demands, equipment types vary widely. Selecting the right one is crucial to the long-term reliability of process manufacturing. Here are the different types of process equipment and specific examples:
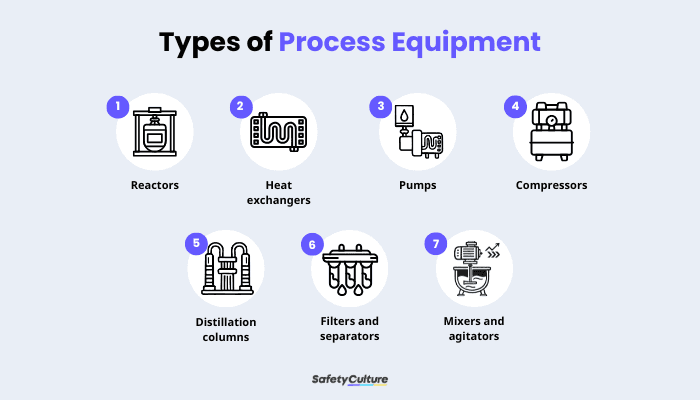
Reactors
Widely used in chemical plants, pharmaceuticals, and petrochemicals, these vessels carry out chemical reactions under controlled conditions such as temperature and pressure.
Processes such as polymerization and vaccine bioreactors require extreme precision. The smallest temperature shift can ruin batches, costing millions. As such, utilizing the right equipment yields high results and avoids wasted runs.
Heat exchangers
Essential in power plants, HVAC systems, oil refineries, and food processing, this transfers her between two or more fluids without mixing them.
Shell and tube exchangers act like a radiator for refiners. They recycle heat. cutting fuel use. It is a must-have because it prevents equipment from overheating while saving millions in energy costs.
Pumps
This moves liquids through pipelines by increasing fluid pressure or flow. It’s a necessary tool across industries, from manufacturing operations (e.g., chemical processing and food production) to utility services (e.g., water treatment, oil and gas).
Choosing the right pump for a particular process or material is vital in preventing clogs and cutting energy use. For instance, centrifugal pumps are for plain water while positive displacement pumps push thick syrups.
Compressors
Commonly found in natural gas processing, refrigeration, and manufacturing plants, this increases the pressure of gases for storage or transport.
In automotive assembly plants, air compressors power the pneumatic robots and wrenches that build cars. Precise pressure prevents assembly errors and reduces energy waste, saving thousands in operational costs daily.
Distillation columns
This separates liquid mixtures based on differences in boiling points. They are critical in oil refineries, chemical production facilities, and alcohol distilleries.
For example,giant fractionating columns in oil refineries sort crude oil into gasoline and diesel. Steady heat control boosts fuel yield, reducing waste and lowering production costs. Liquor producers can also increase alcohol purity and consistency with this equipment.
Filters and separators
Used in wastewater treatment, pharmaceuticals, and food processing, these remove solid particles or separate liquids and gases from process streams.
In bottling plants,membrane filters remove microbes from juice and soda, ensuring a sterile product. Oil-water separators are must-haves in wastewater treatment, turning a potential environmental hazard into usable oil before discharge.
Mixers and agitators
One of the most important process equipment components in the manufacturing system, these ensure liquids, solids, and slurries achieve uniform composition. They are widely used, from chemical manufacturing to food and cosmetics production.
High-shear agitators blend pigments and resins into uniform coatings. The perfect mix targets the right shade and prevents color separation. In commercial bakeries, mixers develop gluten for thousands of loaves. It prevents overmixing, saving facilities thousands of dollars in wasted ingredients.
Which Standards and Regulations Apply to Process Equipment Design and Operation?
To implement effective safety measures when handling process equipment, it’s important to understand the standards and regulations needed for compliance. For example, catastrophes like the Bhopal gas leak and the Texas City refinery explosion were partly due to failures in industrial equipment and systems. Both caused massive loss of life and environmental damage, and more importantly, exposed the need for strict standards. Here are the most relevant:
OSHA 1910.119 Process Safety Management (US) addresses hazardous chemical workflows. It requires hazard analysis, mechanical integrity programs, and employee training.
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (US) is a widely adopted engineering code for pressure-containing equipment. Its focus is on safe design, fabrication, inspection, and testing.
Pressure Systems Safety Regulations (PSSR) (UK) govern pressure systems in operations. Regular inspections, safe operating limits, and maintenance prevent the release of highly hazardous chemicals.
Work Health and Safety Regulations (AU) focus on managing risks associated with high-risk facilities and industrial equipment. It necessitates safe design, operator training, and routine safety checks.
CSA B51 (Canada) requires registration of designs, certified fabrication, and periodic inspections to protect public and worker safety.
Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU (EU) regulates pressure equipment placed on the EU market. Manufacturers and users should follow essential safety requirements, from conformity assessments to technical documentation.
Best Practices for Safety and Usage
Operating complex process equipment is highly challenging, as manufacturers must balance safety, product quality, and regulatory compliance. Applying structured best practices prevents failures that may escalate quickly.
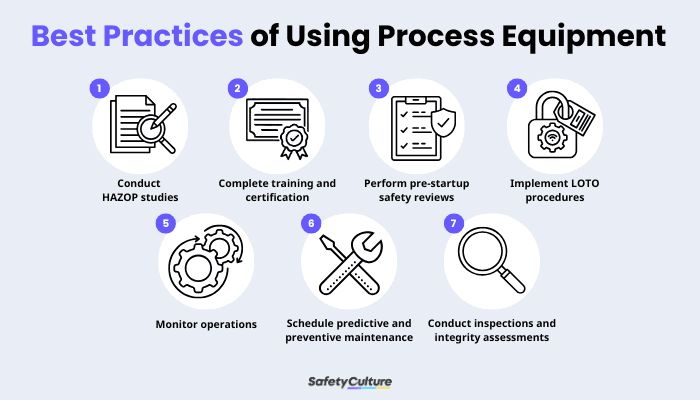
Conduct Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) studies during design and process changes
Systematically identify hazards and failure scenarios before operation. Risks should be addressed proactively, reducing the likelihood of unsafe designs or operating conditions reaching the production stage.
Ensure operator competency through formal training and certification
Train operators on equipment functions, limits, and emergency response. Knowledgeable personnel can detect abnormalities early, follow procedures correctly, and respond safely under abnormal conditions.
Perform pre-startup safety reviews before commissioning or restarting equipment
Verify equipment, controls, safeguards, and procedures prior to operation. Use digital tools like checklists to centralize inspections and maintain a comprehensive log. This confirms readiness, eliminating overlooked hazards, and ensuring all safety systems function as intended before exposure to live processes.
Create your own machinery pre-start checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Implement lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures during maintenance and servicing
Energy sources must be isolated and secured before work begins. This prevents unexpected startup or energy release, protecting process equipment maintenance personnel from serious injury or fatal accidents.
Monitor operations using fixed and portable detection systems
Sensors continuously check for leaks, abnormal temperature and pressure, or hazardous atmospheres. They provide early warnings that help managers and frontline workers implement rapid corrective action before conditions escalate into fires, explosions, or toxic exposures.
Schedule predictive and preventive maintenance based on equipment condition
Plan cleaning, calibrations, testing, and other servicing using performance data, vibration analysis, or wear indicators. Being proactive addresses degradation before failure, minimizing unplanned downtime and extending equipment life.
Conduct regular pressure vessel inspections and integrity assessments
Inspect process equipment for corrosion, cracking, or deformation. This is a crucial component of manufacturing process management, ensuring vessels remain within safe operating limits, preventing catastrophic ruptures and regulatory non-compliance.
Drive Process Equipment Efficiency with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Digitize maintenance schedules, lockout/tagout procedures, and hazard assessments to ensure safety throughout the operations. Centralize training records and leverage analytics when reviewing relevant data for strategizing upgrades, minimizing breakdowns and ensuring regulatory compliance. Reduce unplanned downtime, enhance worker safety, and support continuous improvement across production lines through a unified platform.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Process Equipment
In this article
- What is Process Equipment?
- The Critical Role of Process Equipment
- What are the Common Types of Process Equipment Across Industries?
- Which Standards and Regulations Apply to Process Equipment Design and Operation?
- Best Practices for Safety and Usage
- Drive Process Equipment Efficiency with SafetyCulture
- FAQs About Process Equipment
Related articles
Safety
Safety Management

Transforming Workplaces with AI Safety Inspection
Learn about AI safety inspection and its role in smarter audits, automated insights, and proactive risk management.
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.