Combustible Dust: An Explosion Hazard
Learn more about combustible dust, its elements, examples, and hazards to protect your workplace from dust explosions.

Published 20 Oct 2025
Article by
5 min read
What is Combustible Dust?
Combustible dust is any solid material that is divided into fine or distinct particles, which under certain conditions and concentration, can rapidly catch fire or become explosive once exposed to air and other elements. It can be found in a wide variety of materials in various industries and created when items are handled, transported, processed, or stored. Workplaces and facilities that generate dust are all potentially at risk.
Why is it a Hazard?
According to the latest report released by Dust Safety Science, a combustible hazard research organization, there’s a yearly average of 28 dust explosions, 25 injuries, and a range from one to six fatalities.
One of the notable incidents of dust explosions in the United States is the sugar dust explosion that happened in Georgia in 2008. 14 people were killed in the incident, while 40 people sustained injuries.
These numbers show that dust explosion is still an increasing safety issue in industrial and workplace settings. Businesses should always put safety systems in place to proactively address any issues and prevent these types of incidents that lead to damage to property, injury, and even fatality from ever happening.
Improve your EHS Management
Cultivate a safe working environment and streamline compliance with our EHS solutions.
The Dust Explosion Pentagon
A dust explosion can occur when all of the following five elements are present:
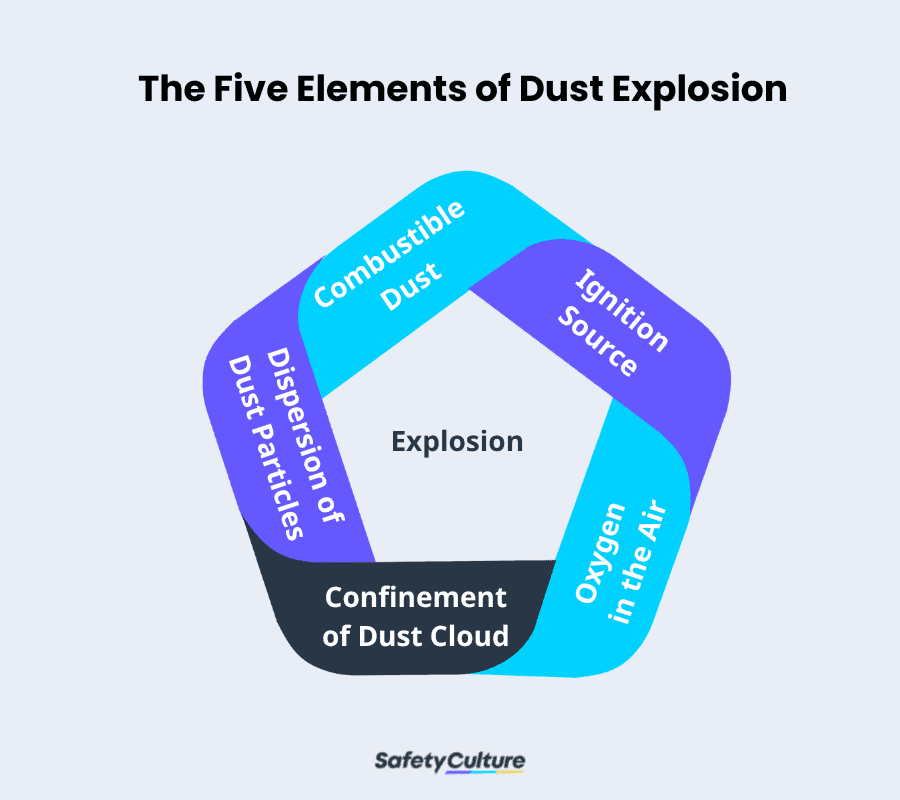
Combustible dust – These are solid materials with fine particles that are susceptible to fire or explosion. This element is often referred to as the fuel.
Ignition source – These are processes or scenarios that can cause fire or explosion, such as electrical sparks, static electricity, hot surfaces, friction, etc.
Oxygen in the air – This is the oxidizing agent in the air. Along with the previous two elements, it’s enough to create a dust fire.
Confinement of dust cloud – For a dust explosion to occur, the dust elements should be confined in an enclosed space where pressure builds and expands.
Dispersion of dust particles – A dust explosion finally happens when all four elements are present and the dust particles are dispersed or distributed in an enclosed area.
Combustible Dust Examples
Workplaces utilize various materials daily and many of these can potentially be combustible dust. Examples of materials include:
Agricultural products such as sugar, powdered milk, corn starch, flour, rice, etc. This puts not just the agricultural industry at risk of dust explosion, but the food production industry as well.
Chemical dust such as coal, sulphur, etc. These types of materials are often present in the pharmaceutical industry.
Textile products such as silk, wool, synthetic fibers, etc. This puts the fabric manufacturing industry at enormous risk of explosion if not regularly monitored.
Wood materials can lead to combustible dust, especially those that are stored and used to manufacture new products.
Metal substances such as aluminum, bronze, magnesium, etc. The businesses that are often at risk with this type of dust hazard are the metal processing and metal manufacturing industries.
How to Prevent Combustible Dust Explosions
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ) released a Hazard Communication Guidance for Combustible Dusts that gives businesses and employers a guide in implementing their control measures for dust explosions.
These are some preventive measures to proactively maintain a safe working environment for employees and in facilities concerning combustible dust:
Identify hazardous dusts present in your workplace.
Recognize all potential combustible materials within your site. Conduct regular inspections to uncover hidden or overlooked substances that could generate hazardous dust. Document every finding to determine how best to manage and eliminate each dust hazard effectively.
Use proper dust collection systems.
Maintain strict housekeeping standards to minimize fire and explosion risks. Use an industrial-grade vacuum designed for combustible dust to collect and safely remove particles from the site. Avoid sweeping or using compressed air, as these can disperse dust into the air and increase ignition risk. Always ensure all dust collection equipment complies with industrial safety standards and is regularly inspected for functionality.
Implement good control measures.
Establish a comprehensive dust control strategy that prevents accumulation and reduces ignition sources. Integrate safety procedures into daily operations, outlining clear steps for monitoring, containment, and removal of dust. Standardize these measures across departments so all employees follow consistent safety protocols.
Conduct regular employee training.
Train all employees regularly on recognizing and handling combustible dust hazards. Include hands-on sessions for operating safety equipment, using extinguishing systems, and managing fire or explosion incidents. Reinforce awareness through refresher courses and visual reminders throughout the facility to maintain safety-conscious behavior.
Assess confined space risks.
Evaluate confined spaces, ducts, silos, and other enclosed areas where dust clouds may accumulate. Perform proactive risk assessments to detect potential explosion hazards and implement control systems before issues escalate. Establish permit systems and ventilation protocols to ensure safe entry and maintenance in confined environments.
Create your own Dust Risk Assessment checklist
Build from scratch or choose from our collection of free, ready-to-download, and customizable templates.
Perform regular inspections.
Inspect all work areas, dust collection systems, and equipment regularly. Verify that housekeeping procedures are being followed and that preventive measures remain effective. Record inspection results,identify weak points, and implement corrective actions promptly to sustain compliance and continuous improvement.
Control Combustible Dusts with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Efficiently manage and streamline all processes related to combustible dusts across your organization. Use a comprehensive EHS software solution to handle dust-related incident management, safety audits, inspections, risk assessments, and waste management. Centralize these activities to ensure consistent monitoring, quick response, and proactive prevention of combustible dust hazards in every facility.
✓ Save time and reduce costs
✓ Stay on top of risks and incidents
✓ Boost productivity and efficiency
✓ Enhance communication and collaboration
✓ Discover improvement opportunities
✓ Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Combustible Dusts
Related articles
Safety
Safety Management

Transforming Workplaces with AI Safety Inspection
Learn about AI safety inspection and its role in smarter audits, automated insights, and proactive risk management.
Food Safety
Safety

Cold Holding: The Ultimate Guide
Learn about cold holding methods for food safety and how it reduces contamination risks across operations.
Food Safety
Safety

A Comprehensive Guide to Natasha’s Law Training
Learn about the process of Natasha’s Law training and how it helps food businesses efficiently meet allergen labeling requirements.