Wind Turbine Maintenance: Reduce Downtime, Boost Output
Proactive and predictive maintenance is critical in wind turbine management. Understand the steps involved and the tools required to keep wind turbines in good working order.

Published 11 Dec 2025
Article by
6 min read
What is Wind Turbine Maintenance?
Wind turbine maintenance refers to the process of keeping wind turbines running smoothly. It involves inspecting critical components such as blades, gearbox, generator, yaw system, brakes, tower, and electrical systems to find issues before they happen.
Wind turbine maintenance tasks usually include turbine inspection, turbine cleaning, turbine lubrication, and turbine repair. Some of these tasks are the following:
Turbine Inspection - The most common type of maintenance. For this, teams use specialized tools to check key components, record measurements, and capture photos for future reference.
Turbine Cleaning - This process involves removing dirt and debris from the blades, nacelle, and generator. It’s usually done by hand, but automated cleaning systems can be used to save time and reduce risk.
Turbine Lubrication - Lubrication involves applying grease or oil to various parts of the turbine. It helps prevent wear and extends the turbine’s lifespan.
Turbine Repair - This process involves fixing or replacing damaged parts such as blades or gearboxes. These repairs are usually carried out during scheduled or preventive maintenance.
Importance of Wind Turbine Maintenance
Wind turbines play a vital role in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and fighting climate change. They generate clean,renewable energy from the wind—but like any machinery, they need regular maintenance to stay safe and efficient. Because turbines are large and powerful, poor maintenance can lead to costly damage or serious injury.
Some of the most common wind turbine problems include worn bearings, broken blades, and cracked gearboxes. While regular maintenance helps prevent these issues, even well-maintained turbines have a limited lifespan of around 20 to 30 years.
What Maintenance Do Wind Turbines Need?
Regular turbine maintenance is essential because wind turbines are exposed to extreme weather conditions every day. Most turbines need servicing at least once every two years, usually carried out by Wind Turbine Technicians or “Windtechs.” Some models, however, require more frequent maintenance than others. For example, Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWTs) often need more care than Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs) because they sit higher off the ground and have larger blades.
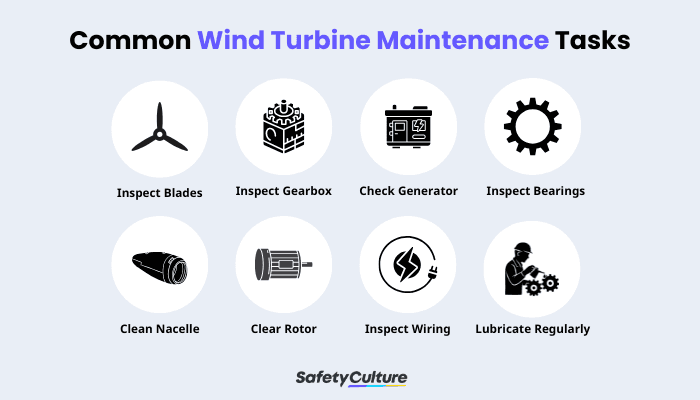
Common Wind Turbine Maintenance Tasks
Here are some common maintenance tasks done for wind turbines:
Check the blades regularly for cracks and damage – Blades can crack over time due to exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures, and corrosion.
Inspect the gearbox regularly for wear and tear – Gearboxes can fail after prolonged use.
Make sure the generator is working correctly – Generators can stop working due to mechanical problems or electrical issues.
Check the bearings regularly – Bearings can become damaged if they aren’t appropriately lubricated.
Clean the nacelle regularly – Nacelles collect dust and debris from the air, which can cause serious health risks.
Keep the rotor free of debris – Debris such as vegetation or sand can get caught in the rotor blades and cause them to break off.
Check the wiring regularly for damage – Wiring can short out and cause fires.
Lubricate regularly – Oil helps keep the gears moving smoothly.
Simplify maintenance scheduling for your business with SafetyCulture
Streamline your operations with usage-based maintenance using our intuitive management software.
How Often Do Wind Turbines Require Maintenance?
Most wind turbines require maintenance every 6 months or at least once a year , though some may only need major servicing every one to two years. However, certain turbines require maintenance more often depending on their operating conditions. Wind Turbine Technicians , often called “Windtechs” in the industry, are responsible for inspecting, servicing, and repairing these turbines.
The frequency of maintenance depends on several factors, including the type of turbine, its age, where it is installed, and how much wind energy it produces. Turbines in harsher environments or with higher usage may need more frequent inspections and repairs to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Some types of wind turbines require more frequent maintenance than others. For example, horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWTs) usually require more maintenance than vertical axis wind turbines (VAWTs).
Horizontal axis wind turbines are designed to capture wind energy from any direction. Their use is most common in areas with strong winds, such as coastal regions. Vertical axis wind turbines are designed for use in areas with weaker winds, such as inland regions.
Achieve operational excellence
Cultivate a culture of excellence with our digital solutions that enhance efficiency, agility, and continuous improvement across all operations.
Common Maintenance Strategies Used
Wind turbine operation and maintenance should be balanced, scheduled, and emergency-based. Because of this, wind technicians must always be prepared to handle any type of maintenance.
Below are some common maintenance strategies that can be applied to ensure wind turbines are fully operational:
Preventative Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is a great way to avoid major problems and downtime before they happen. Regular inspections and routine maintenance for wind turbines should be scheduled weekly, monthly, or annually, depending on the component’s priority. This is especially important for components such as the blades, which can develop erosion or cracks from prolonged environmental exposure.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a strategy that helps predict costly breakdowns by identifying potential problems before they happen. Windtechs need to be prepared for issues that could lead to sudden shutdowns. With the help of modern technology such as asset management systems and sensors that monitor a turbine’s speed, temperature, and vibration, these problems can be fixed early.
Corrective Maintenance
Corrective maintenance involves making repairs on wind turbines after an issue has happened. It is reactive and addresses problems that were not detected or prevented by routine inspections. While preventive and predictive maintenance aim to avoid unexpected breakdowns, corrective maintenance deals with restoring wind turbine functionality as quickly as possible following unplanned issues.
How Does Poor Maintenance Affect a Turbine?
If a wind turbine is poorly maintained, it may not be able to produce electricity at total capacity. The turbine owner must pay for electricity produced when the turbine is not operating at its peak performance.
It is called curtailment. Curtailment occurs because the wind turbine cannot generate enough power to meet the electrical needs of the grid. The cost of this electricity is passed along to the consumer.
Curtailment costs vary depending on the type of wind turbine and the amount of energy generated. Some turbines have a fixed price per kilowatt hour (kWh) of electricity generated, while others have a variable rate based on the prevailing wholesale electricity price.
Many factors influence curtailment rates, including the number of hours the turbine operates each day, the average wind speed during those hours, and the amount of energy the turbine generates.
To avoid curtailment,wind farm owners should keep their turbines well maintained. They should inspect them regularly and perform any necessary repairs or maintenance before they begin producing electricity.
They should also ensure that their turbines operate at maximum efficiency. They should use only quality components, maintain the blades properly, and monitor the entire system’s operation.
Cut Downtime and Keep Turbine Performance High with SafetyCulture
Why use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
Save time and reduce costs
Stay on top of risks and incidents
Boost productivity and efficiency
Enhance communication and collaboration
Discover improvement opportunities
Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Wind Turbine Maintenance
In this article
- What is Wind Turbine Maintenance?
- Importance of Wind Turbine Maintenance
- What Maintenance Do Wind Turbines Need?
- How Often Do Wind Turbines Require Maintenance?
- Common Maintenance Strategies Used
- How Does Poor Maintenance Affect a Turbine?
- Cut Downtime and Keep Turbine Performance High with SafetyCulture
- FAQs About Wind Turbine Maintenance
Related articles
Facility Management
Maintenance

A Guide to Retail Facility Management
Improve store performance with effective retail facility management, and learn its key components, challenges, and top solutions for success.
Equipment Maintenance
Maintenance

Autonomous Vehicle Maintenance for Safety and Asset Performance
Discover how autonomous vehicle maintenance supports safety, reliability, and asset performance through preventative workflows.
Maintenance
Equipment Maintenance

Understanding Mechanical Integrity and Its Importance
Understand the meaning of mechanical integrity, its fundamental components, and how to develop a mechanical integrity plan for the team.