A Comprehensive Guide to Electric Vehicle Battery Management
Understand how electric vehicle battery management works to monitor, protect, and optimize batteries for smarter, safer, and more sustainable fleets.

Published 24 Oct 2025
Article by
7 min read
What is Electric Vehicle Battery Management?
Electric Vehicle (EV) battery management is a strategic system to maximize battery value and lifespan. It involves data-driven monitoring of temperature and power levels, operational planning, and regular health assessment to improve energy efficiency, ensure safe fleet performance, and maximize battery lifespan.
Carefully managing EV batteries with a data-driven approach achieves more than just operational efficiency. It provides companies with significant cost savings, improves decisions about fleet health and residual value, and ensures rigorous compliance with evolving regulations.
Key Components and Core Functions
Fueled by the transition to electric mobility and large-scale renewable energy adoption, global demand for batteries surged by over 40% in 2023. The surge highlights the importance of effective EV battery management, which is key to ensuring safe, efficient, and sustainable operation for every battery in the fleet. Learn what this specific framework in the EV fleet management involves:
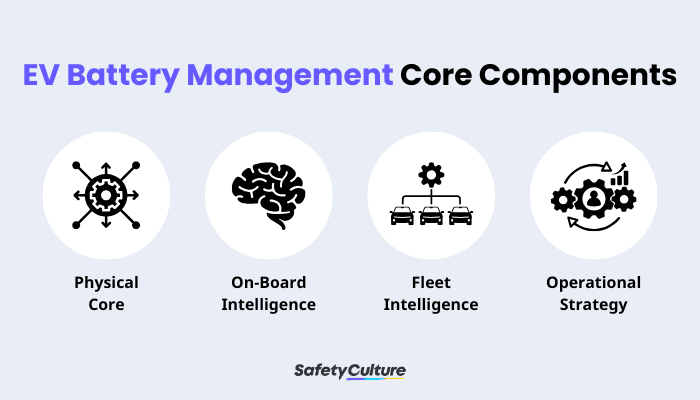
EV Battery Management Core Components
Physical Core
As the foundation of EV battery management, the physical core consisting of battery cells, modules, and packs defines the fleet's total energy capacity and life cycle potential. This is the most important part of the battery. With the 65% increase in demand for lithium-ion batteries, the need for swapping or repurposing systems helps lower costs, minimize waste, and ensure energy security across fleet operations.
On-Board Intelligence
The in-vehicle Battery Management System (BMS) acts as the “brain” of the EV’s energy system. Integrated with the following functions, it detects anomalies, prevents failures, and informs higher-level analytics and maintenance decisions:
Real-time monitoring sensors measure cell voltage, current, and temperature.
Cell balancing ensures uniform performance across sales to maintain consistent output.
Thermal management of electric vehicle battery systems (cooling and heating systems) stabilizes temperature for optimal performance.
Charging and discharging regulation coordinates energy flow to prevent stress on battery cells.
Protection mechanisms safeguard against overcharge, overdischarge, overcurrent, and overheating.
Fleet Intelligence
Raw data from the BMS is converted into actionable insights, ensuring every vehicle operates at peak efficiency. Utilizing a centralized telematics and analytics network is crucial to aggregate data from every vehicle's BMS, optimizing overall fleet utilization and reducing unplanned downtimes.
Operational Strategy
This component governs how to manage energy, assets, and performance across the EV fleet, aligning technical performance with financial and environmental goals. Through the following, companies can reduce operating costs, enhance sustainability, and ensure regulatory compliance:
Fleet energy and charging optimization involves coordinating charging schedules, energy distribution, and grid interaction,supported by ISO 15118 ,to minimize costs and peak demand.
Battery residual value tracking assesses and maximizes the remaining economic value of used batteries.
State of Health (SoH) certification provides verified metrics for reselling, reusing, or recycling batteries.
Explore SafetyCulture Monitoring Solution
Utilize advanced sensor technology to monitor assets, automate vital alerts, implement actions, and report urgent issues.
Regulations in Electric Vehicle Battery Management
Battery recycling and end-of-life management are gaining critical importance for EV fleets, driving sustainability, reducing environmental harm, and enabling resource recovery. Addressing specific aspects such as functional safety and post-crash protocols is also vital to comply with these key regulations and standards:
IEC 61508 (Functional Safety Standard) is foundational in the functional safety of BMS design for automotive and industrial applications, ensuring reliable and safe battery operations.
ISO 26262 (Automotive Functional Safety) mandates rigorous safety processes for automotive electronic systems, guiding hazard analysis, safety goal verification, and protection for high-voltage systems.
UL 1973 specifies requirements for stationary and automotive batteries, including design and testing criteria to ensure batteries in EVs are safe under normal and abnormal conditions.
EU CO₂ Emissions Regulations limit fleet emissions, pressuring operators to adopt EVs with efficient BMS to comply with greenhouse gas reduction targets and sustainability goals.
SAE International BMS Standards , developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers, outline key technical and safety guidelines for battery management.
Battery passport and traceability regulations are emerging in regions like the EU and China to ensure ethical sourcing and lifecycle management for EV batteries.
Post-crash protocols, which include disconnecting high-voltage battery circuits to prevent fires or electric shocks, are currently being developed by organizations, like the National Fire Protection Association and similar departments, worldwide.
EV charging leaders like Blink Charging and BP Pulse UK leverage advanced software solutions to build a robust, digital management framework. Gaining real-time visibility into field operations and enabling rapid communication of safety protocols, they can ensure compliance across their rapidly expanding and geographically dispersed EV infrastructure.
Challenges in Managing Electric Vehicle Batteries
While many companies are eager to transition to EVs, key challenges and safety risks often slow their progress. Understanding these obstacles is the first step to solving them:
High battery costs and limited specific energy - Companies fail to scale their EV fleet because batteries are expensive. The capacity per weight (specific energy) also constrains vehicle range and payload flexibility.
Battery degradation - While frequent fast charging offers greater convenience, the intense heat generated during these sessions accelerates the chemical processes within the battery. This leads to faster degradation and capacity loss.
Inaccurate estimation of State of Charge (SoC) and SoH - Measuring precise SoC and SoH is critical for the operations, but remains complex. Doing so requires sophisticated algorithms and sensor integration.
Thermal runaway, fire, and other environmental hazards - Lithium-ion batteries pose safety risks, like explosions and toxic material leaks. These risks must always be taken into consideration
Infrastructure and operational constraints - Varied environmental conditions and limited charging infrastructure could affect battery performance and the company’s overall operations. Daily operational tasks can also be a challenge for efficient battery management.
Key Capabilities of Modern EV Battery Management Solutions
The success of EV fleets does not just rely on high-performing batteries. It also requires smart digital systems that monitor, analyze, and optimize every stage of battery use. Here are the key capabilities of digital tools in EV battery management and how they enhance fleet performance.
Digital Asset Management : A centralized software platform provides a digital record of each asset's location, usage history, performance data, and maintenance status. This capability enables fleet battery health monitoring, tracking metrics such as capacity, cycle count, SoH, and charging patterns.
Automated Maintenance Scheduling: With sensor data from the BMS (e.g., usage patterns in degradation rates), this tool automatically triggers service or inspection tasks. Integrating this with EV charging infrastructure management ensures that vehicles are serviced during low demand after charging cycles.
Predictive and Preventive Maintenance: Advanced analytics, powered by machine learning and based on historical data trends, anticipates potential failures (e.g., voltage irregularities, temperature fluctuations, charge-discharge cycles) before they occur. These also help in implementing best practices or changing them as needed.
Digital Inspections and Checklists: Fleet operators and technicians can utilize predefined vehicle inspection checklists for battery safety, thermal performance, and charging systems. This replaces subjective and error-prone paper-based inspection forms for consistent reporting, keeping, and auditable documentation for compliance.
Incident and Issue Management: When faults and anomalies are detected (e.g., overheating, communication failure, charging errors), this digital tool helps personnel identify, report, and resolve safety-critical issues rapidly. It also automatically logs the incident for continuous progress tracking and record-keeping.
Training and Knowledge Sharing: Technicians need on-demand access to EV digital manuals , voice tutorials, and interactive modules that guide them with maintenance, charging safety, and software use. This repository of digital knowledge supports continuous learning as technologies and regulations evolve.
Integration and Scalability: Consolidating data from batteries, charging stations, telematics platforms, and fleet operations into one ecosystem simplifies large-scale fleet management and prepares the system for future expansion, even with autonomous vehicles . It also supports regulatory compliance and audit trails.
Optimize Electric Vehicle Battery Performance and Value with SafetyCulture
Why Use SafetyCulture?
SafetyCulture is a mobile-first operations platform adopted across industries, such as manufacturing, mining, construction, retail, and hospitality. It’s designed to equip leaders and working teams with the knowledge and tools to do their best work—to the safest and highest standard.
Streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, enhance resource utilization, and build an agile and scalable infrastructure with SafetyCulture. Strive for operational excellence to boost competitive advantage, foster sustainable growth, and deliver long-term value.
Save time and reduce costs
Stay on top of risks and incidents
Boost productivity and efficiency
Enhance communication and collaboration
Discover improvement opportunities
Make data-driven business decisions
FAQs About Electric Vehicle Battery Management
In this article
- What is Electric Vehicle Battery Management?
- Key Components and Core Functions
- Regulations in Electric Vehicle Battery Management
- Challenges in Managing Electric Vehicle Batteries
- Key Capabilities of Modern EV Battery Management Solutions
- Optimize Electric Vehicle Battery Performance and Value with SafetyCulture
- FAQs About Electric Vehicle Battery Management
Related articles
Transportation
Automotive

A Comprehensive Guide to Delivery Driver Training
Learn how delivery driver training improves safety, consistency, and frontline readiness across fleets while reducing operational risk.
Automotive
Transportation

Driver Training: How to Improve Safety
Discover driver training programs, understand safety requirements, and learn which certifications are needed for specific industrial roles.
Transportation
Automotive

ISO 15118: The Future of Smart EV Charging
Learn what ISO 15118 is, how it powers Plug & Charge technology, and why it is becoming essential for charging networks worldwide.